GPT2 mutations in autosomal recessive developmental disability: extending the clinical phenotype and population prevalence estimates
- PMID: 31471722
- PMCID: PMC6748651
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-019-02057-x
GPT2 mutations in autosomal recessive developmental disability: extending the clinical phenotype and population prevalence estimates
Abstract
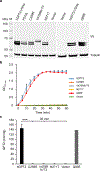
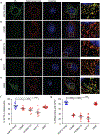
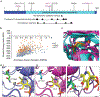
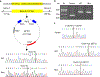
The glutamate pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2) gene produces a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the reversible transfer of an amino group from glutamate to pyruvate, generating alanine and alpha-ketoglutarate. Recessive mutations in GPT2 have been recently identified in a new syndrome involving intellectual and developmental disability (IDD), postnatal microcephaly, and spastic paraplegia. We have identified additional families with recessive GPT2 mutations and expanded the phenotype to include small stature. GPT2 loss-of-function mutations were identified in four families, nine patients total, including: a homozygous mutation in one child [c.775T>C (p.C259R)]; compound heterozygous mutations in two siblings [c.812A>C (p.N271T)/c.1432_1433delGT (p.V478Rfs*73)]; a novel homozygous, putative splicing mutation [c.1035C>T (p.G345=)]; and finally, a recurrent mutation, previously identified in a distinct family [c.1210C>T (p.R404*)]. All patients were diagnosed with IDD. A majority of patients had remarkably small stature throughout development, many < 1st percentile for height and weight. Given the potential biological function of GPT2 in cellular growth, this phenotype is strongly suggestive of a newly identified clinical susceptibility. Further, homozygous GPT2 mutations manifested in at least 2 of 176 families with IDD (approximately 1.1%) in a Pakistani cohort, thereby representing a relatively common cause of recessive IDD in this population, with recurrence of the p.R404* mutation in this population. Based on variants in the ExAC database, we estimated that approximately 1 in 248 individuals are carriers of moderately or severely deleterious variants in GPT2.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2004) Economic costs associated with mental retardation, cerebral palsy, hearing loss, and vision impairment--United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 53:57–59. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013) Intellectual Disability Among Children https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/developmentaldisabilities/documents/Intellect.... Accessed on 10 October 2018
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

