Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Osteoclast Activity and Bone Density in Morbidly Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 31471767
- PMCID: PMC7515205
- DOI: 10.1007/s11695-019-04154-2
Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Osteoclast Activity and Bone Density in Morbidly Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is a well-established treatment for morbid obesity and type 2 diabetes. The effects of RYGB on bone metabolism and bone health are largely unknown.
Objective: Determine the changes in osteoclast function and bone density 1 year after RYGB as compared with a control group undergoing a diabetes support and education program (DSE).
Design: A prospective cohort study with patients matched for weight and age assigned to RYGB or DSE.
Setting: Large academic institution.
Patients or other participants: Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and morbid obesity (body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2).
Intervention: Subjects either received laparoscopic RYBG or DSE, which consisted of nutritional, exercise, and dietary counseling performed by a certified diabetic educator and a nutritionist three times over a year.
Main outcome measure: Osteoclast activity, bone mineral density.
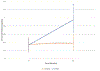
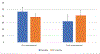
Results: One year after, intervention subjects undergoing RYGB have a 280% increase in osteoclast activity as compared with a 7.6% increase in the DSE control group (P < 0.001). Furthermore, there was a statistically significant increase in sclerostin levels in subjects undergoing RYGB compared with an increase in the control group. The total bone mineral density was statistically unchanged within 1 year of intervention in both groups. A statistically significant decrease in bone mineral density in the left ribs (decrease of 6.8%, P < 0.05) and lumbar spine (decrease of 4.0%, P < 0.05) was seen 1 year after RYGB.
Conclusions: There is a significant increase in osteoclast activity observed 1 year after RYGB; the long-term clinical implications of this increased bone metabolism are unknown.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Bone loss; Bone mineral density; Osteoclast; Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2008. Obes Surg. 2009;19(12):1605–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

