Activity of methylgerambullin from Glycosmis species (Rutaceae) against Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia duodenalis in vitro
- PMID: 31472356
- PMCID: PMC6722286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2019.08.001
Activity of methylgerambullin from Glycosmis species (Rutaceae) against Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia duodenalis in vitro
Abstract
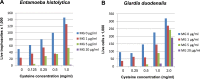
Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia duodenalis are widespread intestinal protozoan parasites which both spread via cysts that have to be ingested to infect a new host. Their environment, the small intestine for G. duodenalis and the colon for E. histolytica, contains only very limited amounts of oxygen, so both parasites generate energy by fermentation and substrate level phosphorylation rather than by oxidative phosphorylation. They both contain reducing agents able to reduce and activate nitroimidazole drugs such as metronidazole which is the gold standard drug to treat Entamoeba or Giardia infections. Although metronidazole works well in the majority of cases, it has a number of drawbacks. In animal models, the drug has carcinogenic activity, and concerns about a possible teratogenic activity remain. In addition, the treatment of G. duodenalis infections is hampered by emerging metronidazole resistance. Plant-derived drugs play a dominant role in human medicine, therefore we tested the activity of 14 isolated plant compounds belonging to seven different classes in vitro against both parasites. The tests were performed in a new setting in microtiter plates under anaerobic conditions. The compound with the highest activity was methylgerambullin, a sulphur-containing amide found in Glycosmis species of the family Rutaceae with an EC50 of 14.5 μM (6.08 μg/ml) after 24 h treatment for E. histolytica and 14.6 μM (6.14 μg/ml) for G. duodenalis. The compound was successfully synthesised in the laboratory which opens the door for the generation of new derivatives with higher activity.
Keywords: Aglafoline; Entamoeba histolytica; Giardia duodenalis; Glycosmis spp.; Methylgerambullin; Sulphur-containing amide.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of new 5-nitroimidazoles against metronidazole-susceptible and -resistant Giardia, Trichomonas, and Entamoeba spp.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Jan;43(1):73-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.1.73. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 9869568 Free PMC article.
-
Drug targets and mechanisms of resistance in the anaerobic protozoa.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001 Jan;14(1):150-64. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.1.150-164.2001. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11148007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Larrea tridentata: A novel source for anti-parasitic agents active against Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia and Naegleria fowleri.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Aug 9;11(8):e0005832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005832. eCollection 2017 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28793307 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility of Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia to plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Dec 6;108(3):367-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.05.025. Epub 2006 Jun 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16846708
-
Reprofiled drug targets ancient protozoans: drug discovery for parasitic diarrheal diseases.Gut Microbes. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):66-71. doi: 10.4161/gmic.22596. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Gut Microbes. 2013. PMID: 23137963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of anti-Entamoeba histolytica activity of medicinal plants published in the last 20 years.Parasitology. 2021 May;148(6):672-684. doi: 10.1017/S0031182021000172. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Parasitology. 2021. PMID: 33536098 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural Alterations of the Human Pathogen Giardia intestinalis after Drug Treatment.Pathogens. 2023 Jun 7;12(6):810. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12060810. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37375500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amoebic Liver Abscess: A disease native to Oman?Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2022 May;22(2):253-256. doi: 10.18295/squmj.6.2021.083. Epub 2022 May 26. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2022. PMID: 35673298 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative phytochemistry of flavaglines (= rocaglamides), a group of highly bioactive flavolignans from Aglaia species (Meliaceae).Phytochem Rev. 2022;21(3):725-764. doi: 10.1007/s11101-021-09761-5. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Phytochem Rev. 2022. PMID: 34104125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broad anti-pathogen potential of DEAD box RNA helicase eIF4A-targeting rocaglates.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 8;13(1):9297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35765-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37291191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdullah R., Rahmani M., Ali A.M., Ismail H.B.M., Sukari M.A., Lian G.E.C., Kulip J. Chemical constituents and biological actvities of Glycosmis chlorosperma var Elmeri (Merr.) stone (Rutaceae) Malays. J. Sci. 2006;25:45–51.
-
- Astelbauer F., Gruber M., Brem B., Greger H., Obwaller A., Wernsdorfer G., Congpuong K., Wernsdorfer W.H., Walochnik J. Activity of selected phytochemicals against Plasmodium falciparum. Acta Trop. 2012;123:96–100. http://www.dx.doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.04.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

