Dynamic re-weighting of acoustic and contextual cues in spoken word recognition
- PMID: 31472578
- PMCID: PMC7273512
- DOI: 10.1121/1.5119271
Dynamic re-weighting of acoustic and contextual cues in spoken word recognition
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Dynamic re-weighting of acoustic and contextual cues in spoken word recognition [J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 146(2), EL135-EL140 (2019)].J Acoust Soc Am. 2023 Jul 1;154(1):48-49. doi: 10.1121/10.0019956. J Acoust Soc Am. 2023. PMID: 37403996 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
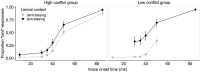
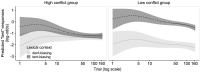
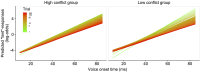
Listeners integrate acoustic and contextual cues during word recognition. However, experiments investigating this integration disrupt natural cue correlations. It was investigated whether changes in correlational structure affect listeners' relative cue weightings. Two groups of participants engaged in a word recognition task. In one group, acoustic (voice onset time) and contextual (lexical bias) cues followed natural correlations; in the other, cues were uncorrelated. When cues were correlated, cue weights were stable throughout the experiment; when cues were uncorrelated, contextual cues were down-weighted. Listeners thus can re-weight cues based on their statistical structure. Studies failing to account for re-weighting risk over/under-estimating cue importance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perceptual Cue Weighting Matters in Real-Time Integration of Acoustic Information During Spoken Word Recognition.Cogn Sci. 2024 Dec;48(12):e70026. doi: 10.1111/cogs.70026. Cogn Sci. 2024. PMID: 39692598
-
Integration of pragmatic and phonetic cues in spoken word recognition.J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 2012 Jul;38(4):967-83. doi: 10.1037/a0026786. Epub 2012 Jan 16. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 2012. PMID: 22250908 Free PMC article.
-
Low-frequency fine-structure cues allow for the online use of lexical stress during spoken-word recognition in spectrally degraded speech.J Acoust Soc Am. 2017 Jan;141(1):373. doi: 10.1121/1.4972569. J Acoust Soc Am. 2017. PMID: 28147573 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between distal speech rate, linguistic knowledge, and speech environment.Psychon Bull Rev. 2015 Oct;22(5):1451-7. doi: 10.3758/s13423-015-0820-9. Psychon Bull Rev. 2015. PMID: 25794478
-
Prosodic cue weighting in the processing of ambiguous sentences by native English listeners and Korean listeners of English.J Acoust Soc Am. 2022 Jan;151(1):158. doi: 10.1121/10.0009171. J Acoust Soc Am. 2022. PMID: 35105020
Cited by
-
Do They Know It's Christmash? Lexical Knowledge Directly Impacts Speech Perception.Cogn Sci. 2024 May;48(5):e13449. doi: 10.1111/cogs.13449. Cogn Sci. 2024. PMID: 38773754 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of subcategorical information during speech perception: revisiting misunderstood limitations.J Mem Lang. 2025 Feb;140:104565. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2024.104565. Epub 2024 Sep 20. J Mem Lang. 2025. PMID: 39430798
-
Mishearing as a Side Effect of Rational Language Comprehension in Noise.Front Psychol. 2021 Sep 6;12:679278. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.679278. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34552526 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving competing predictions in speech: How qualitatively different cues and cue reliability contribute to phoneme identification.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2024 Apr;86(3):942-961. doi: 10.3758/s13414-024-02849-y. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2024. PMID: 38383914 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral degradation and carrier sentences increase age-related temporal processing deficits in a cue-specific manner.J Acoust Soc Am. 2024 Jun 1;155(6):3983-3994. doi: 10.1121/10.0026434. J Acoust Soc Am. 2024. PMID: 38934563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bushong, W. , and Jaeger, T. F. (2017). “ Maintenance of perceptual information in speech perception,” Thirty-Ninth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society.
-
- Christiansen, M. H. , and Chater, N. (2016). “ The now-or-never bottleneck: A fundamental constraint on language,” Behav. Brain Sci. 39, 1–72. - PubMed
-
- Connine, C. M. , Blasko, D. G. , and Hall, M. (1991). “ Effects of subsequent sentence context in auditory word recognition: Temporal and linguistic constraints,” J. Memory Lang. 30(1), 234–250.10.1016/0749-596X(91)90005-5 - DOI
-
- Dahan, D. (2010). “ The time course of interpretation in speech comprehension,” Current Direct. Psychol. Sci. 19(2), 121–126.10.1177/0963721410364726 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

