The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Microvesicles on the Treatment of Experimental CCL4 Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats
- PMID: 31474025
- PMCID: PMC6881047
- DOI: 10.15283/ijsc18143
The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Microvesicles on the Treatment of Experimental CCL4 Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats
Abstract
Background and objectives: The release of microvesicles (MVs) from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been implicated in intercellular communication, and may contribute to beneficial paracrine effects of stem cell-based therapies. We investigated the effect of administration of MSC-MVs on the therapeutic potential of carbon tetrachloride (CCL4) induced liver fibrosis in rats.
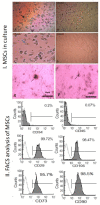
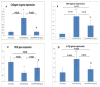
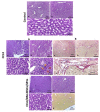
Methods: Our work included: isolation and further identification of bone marrow MSC-MVs by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Liver fibrosis was induced in rats by CCl4 followed by injection of prepared MSC-MVs in injured rats. The effects of MSC-MVs were evaluated by biochemical analysis of liver functions, RNA gene expression quantitation for collagen-1α, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by real time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) techniques. Finally histopathological examination of the liver tissues was assessed for all studied groups.
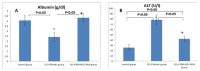
Results: BM-MSC-MVs treated group showed significant increase in serum albumin levels, VEGF quantitative gene expression (p<0.05), while it showed a significant decrease in serum alanine transaminase (ALT) enzyme levels, quantitative gene expression of TGF-β, collagen-1α, IL-1β compared to CCL4 fibrotic group (p<0.05). Additionally, the histopathological assessment of the liver tissues of BM-MSC-MVs treated group showed marked decrease in the collagen deposition & improvement of histopathological picture in comparison with CCL4 fibrotic group.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that BM-MSC-MVs possess anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and pro-angiogenic properties which can promote the resolution of CCL4 induced liver fibrosis in rats.
Keywords: Liver fibrosis; Mesenchymal stem cells; Microvesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment Efficiency of Different Routes of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection in Rat Liver Fibrosis Model.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2161-2171. doi: 10.1159/000492558. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30114694
-
Differentially expressed microRNAs in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in young and older rats and their effect on tumor growth factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HK2 cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Sep 28;6:185. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0179-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26415502 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between the Regenerative and Therapeutic Impacts of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Pre-Treated with Melatonin on Liver Fibrosis.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 1;14(3):297. doi: 10.3390/biom14030297. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540717 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Microvesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Lung Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:985814. doi: 10.1155/2015/985814. Epub 2015 May 12. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26064975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvesicles: the functional mediators in sorafenib resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 23;5(3):749-761. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2021.137. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36176764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium Hydrosulfide Modification of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomes Improves Liver Function in CCL4-Induced Hepatic Injury in Mice.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Jan;11(4):644-655. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.11.4.644. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37131889 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Microvesicles as Potential Vaccine Candidates.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 24;22(3):1142. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031142. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pooled Analysis of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Therapy for Liver Disease in Preclinical Models.J Pers Med. 2023 Feb 28;13(3):441. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030441. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36983624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recellularization of Native Tissue Derived Acellular Scaffolds with Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Cells. 2021 Jul 15;10(7):1787. doi: 10.3390/cells10071787. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of modified mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in the treatment of liver injury.Physiol Res. 2021 Jul 12;70(3):327-343. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934623. Epub 2021 May 12. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33982583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rengasamy M, Singh G, Fakharuzi NA, Siddikuzzaman, Balasubramanian S, Swamynathan P, Thej C, Sasidharan G, Gupta PK, Das AK, Rahman AZA, Fakiruddin KS, Nian LM, Zakaria Z, Majumdar AS. Transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells reduces liver fibrosis more effectively than Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:143. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0595-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kharaziha P, Hellström PM, Noorinayer B, Farzaneh F, Aghajani K, Jafari F, Telkabadi M, Atashi A, Honardoost M, Zali MR, Soleimani M. Improvement of liver function in liver cirrhosis patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection: a phase I–II clinical trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21:1199–1205. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32832a1f6c. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

