Single-Cell Analysis of Crohn's Disease Lesions Identifies a Pathogenic Cellular Module Associated with Resistance to Anti-TNF Therapy
- PMID: 31474370
- PMCID: PMC7060942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.008
Single-Cell Analysis of Crohn's Disease Lesions Identifies a Pathogenic Cellular Module Associated with Resistance to Anti-TNF Therapy
Abstract
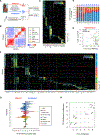
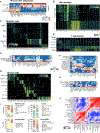
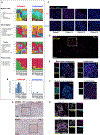
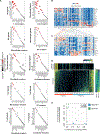
Clinical benefits of cytokine blockade in ileal Crohn's disease (iCD) are limited to a subset of patients. Here, we applied single-cell technologies to iCD lesions to address whether cellular heterogeneity contributes to treatment resistance. We found that a subset of patients expressed a unique cellular module in inflamed tissues that consisted of IgG plasma cells, inflammatory mononuclear phagocytes, activated T cells, and stromal cells, which we named the GIMATS module. Analysis of ligand-receptor interaction pairs identified a distinct network connectivity that likely drives the GIMATS module. Strikingly, the GIMATS module was also present in a subset of patients in four independent iCD cohorts (n = 441), and its presence at diagnosis correlated with failure to achieve durable corticosteroid-free remission upon anti-TNF therapy. These results emphasize the limitations of current diagnostic assays and the potential for single-cell mapping tools to identify novel biomarkers of treatment response and tailored therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; high-dimensional profiling; inflammatory bowel disease; molecular classification; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Unique cellular module identified in Crohn's disease.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Nov;16(11):648-649. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0213-z. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31548711 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aird WC (2007). Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ. Res. 100, 174–190. - PubMed
-
- Bamba S, Andoh A, Yasui H, Makino J, Kim S, and Fujiyama Y (2003). Regulation of IL-11 expression in intestinal myofibroblasts: role of c-Jun AP-1-and MAPK-dependent pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 285, G529–G538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19 AI128949/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA224319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023547/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI137244/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062422/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA078207/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK111995/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI118644/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

