The effect of cysteine oxidation on DJ-1 cytoprotective function in human alveolar type II cells
- PMID: 31474749
- PMCID: PMC6717737
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1833-5
The effect of cysteine oxidation on DJ-1 cytoprotective function in human alveolar type II cells
Abstract
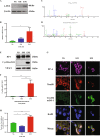
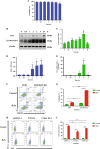
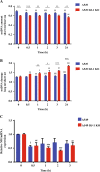
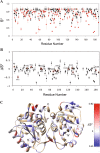
DJ-1 is a multifunctional protein with cytoprotective functions. It is localized in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and mitochondria. The conserved cysteine residue at position 106 (Cys106) within DJ-1 serves as a sensor of redox state and can be oxidized to both the sulfinate (-SO2-) and sulfonate (-SO3-) forms. DJ-1 with Cys106-SO2- has cytoprotective activity but high levels of reactive oxygen species can induce its overoxidation to Cys106-SO3-. We found increased oxidative stress in alveolar type II (ATII) cells isolated from emphysema patients as determined by 4-HNE expression. DJ-1 with Cys106-SO3- was detected in these cells by mass spectrometry analysis. Moreover, ubiquitination of Cys106-SO3- DJ-1 was identified, which suggests that this oxidized isoform is targeted for proteasomal destruction. Furthermore, we performed controlled oxidation using H2O2 in A549 cells with DJ-1 knockout generated using CRISPR-Cas9 strategy. Lack of DJ-1 sensitized cells to apoptosis induced by H2O2 as detected using Annexin V and propidium iodide by flow cytometry analysis. This treatment also decreased both mitochondrial DNA amount and mitochondrial ND1 (NADH dehydrogenase 1, subunit 1) gene expression, as well as increased mitochondrial DNA damage. Consistent with the decreased cytoprotective function of overoxidized DJ-1, recombinant Cys106-SO3- DJ-1 exhibited a loss of its thermal unfolding transition, mild diminution of secondary structure in CD spectroscopy, and an increase in picosecond-nanosecond timescale dynamics as determined using NMR. Altogether, our data indicate that very high oxidative stress in ATII cells in emphysema patients induces DJ-1 overoxidation to the Cys106-SO3- form, leading to increased protein flexibility and loss of its cytoprotective function, which may contribute to this disease pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

