Complications of endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic fluid collections and their management
- PMID: 31474789
- PMCID: PMC6686089
- DOI: 10.20524/aog.2019.0404
Complications of endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic fluid collections and their management
Abstract
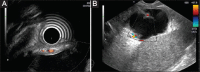
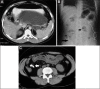
The development of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided drainage techniques and lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) has markedly reduced the complication rate of endoscopic transmural drainage of pancreatic collections and made these procedures safer and more effective. Despite its improved safety profile, various types of complications, some even life-threatening, can occur after EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Stent maldeployment/migration, bleeding, gastrointestinal perforation, and air embolism are important complications of EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic collections. Delayed complications weeks after the procedure, such as bleeding and buried LAMS due to the presence of prolonged indwelling transmural stents, have also been described. Careful patient selection, with proper assessment of the size, solid necrotic content and location of the collection, as well as an in-depth understanding of various risk factors that predict complications, are important for a safer and more effective endoscopic transmural drainage. For a better clinical outcome, it is important for the endoscopist to know about various complications of EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic collections, as well as their appropriate management strategies.
Keywords: Endosonography; bleeding; embolism; perforation; pseudoaneurysm; stents.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures




References
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012:revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Cui ML, Kim KH, Kim HG, et al. Incidence, risk factors and clinical course of pancreatic fluid collections in acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:1055–1062. - PubMed
-
- Rana SS, Sharma RK, Gupta P, Gupta R. Natural course of asymptomatic walled off pancreatic necrosis. Dig Liver Dis. 2019;51:730734. - PubMed
-
- Rana SS. An overview of walled-off pancreatic necrosis for clinicians. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13:331–343. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
