Role of the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Signaling Pathway in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 31474876
- PMCID: PMC6702336
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01038
Role of the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Signaling Pathway in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
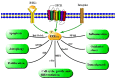
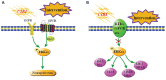
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), an important member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, is found in many organisms, and it participates in intracellular signal transduction. Various stimuli induce phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in vivo and in vitro. Phosphorylated ERK1/2 moves to the nucleus, activates many transcription factors, regulates gene expression, and controls various physiological processes, finally inducing repair processes or cell death. With the aging of the population around the world, the occurrence of ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), especially in the brain, heart, kidney, and other important organs, is becoming increasingly serious. Abnormal activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is closely related to the development and the metabolic mechanisms of IRI. However, the effects of this signaling pathway and the underlying mechanism differ between various models of IRI. This review summarizes the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and the molecular mechanism underlying its role in models of IRI in the brain, heart, liver, kidneys, and other organs. This information will help to deepen the understanding of ERK1/2 signals and deepen the exploration of IRI treatment based on the ERK1/2 study.
Keywords: ERK1/2 signaling pathway; damage effect; ischemia-reperfusion injury; molecular mechanism; protective effect; therapeutic target.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1- and 2-mediated gastric mucosal injury and repair in gastric ischemia-reperfusion of rats.J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec;41(12):1158-68. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1902-2. Epub 2007 Feb 6. J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17287895
-
Cardiac-Specific SOCS3 Deletion Prevents In Vivo Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury through Sustained Activation of Cardioprotective Signaling Molecules.PLoS One. 2015 May 26;10(5):e0127942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127942. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26010537 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase and big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 by ischemia/reperfusion and oxidative stress in perfused guinea pig hearts.Circ Res. 1999 Dec 3-17;85(12):1164-72. doi: 10.1161/01.res.85.12.1164. Circ Res. 1999. PMID: 10590243
-
The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 8;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122001. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27941647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in neurological diseases: A potential therapeutic target (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jun;39(6):1338-1346. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2962. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28440493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin as a therapy in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: Potential mechanisms by which MT2 activation mediates cardioprotection.J Adv Res. 2020 Sep 28;29:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.09.007. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 33842003 Free PMC article.
-
Sennoside A Induces GLP-1 Secretion Through Activation of the ERK1/2 Pathway in L-Cells.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Apr 29;13:1407-1415. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S247251. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32425572 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Relevance of Secondary Intracellular Signaling Cascades Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 24;25(11):5708. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115708. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Responses of the Eukaryotic Cell Line INT407 on the Internalized Campylobacter jejuni-The Other Side of the Coin.Pathogens. 2024 May 7;13(5):386. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13050386. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38787238 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of High-Sensitivity CRP Level on the No-Reflow Phenomenon in STEMI Patients.Cardiol Res Pract. 2025 Jun 30;2025:9359830. doi: 10.1155/crp/9359830. eCollection 2025. Cardiol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40667402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

