Estrogens, Estrogen Receptors Effects on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria
- PMID: 31474941
- PMCID: PMC6702264
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00557
Estrogens, Estrogen Receptors Effects on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria
Abstract
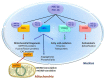
Mitochondria are unique organelles present in almost all cell types. They are involved not only in the supply of energy to the host cell, but also in multiple biochemical and biological processes like calcium homeostasis, production, and regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), pH control, or cell death. The importance of mitochondria in cell biology and pathology is increasingly recognized. Being maternally inherited, mitochondria exhibit a tissue-specificity, because most of the mitochondrial proteins are encoded by the nuclear genome. This renders them exquisitely well-adapted to the physiology of the host cell. It is thus not surprising that mitochondria show a sexual dimorphism and that they are also prone to the influence of sex chromosomes and sex hormones. Estrogens affect mitochondria through multiple processes involving membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors (ERs) as well as more direct effects. Moreover, estrogen receptors have been identified within mitochondria. The effects of estrogens on mitochondria comprise protein content and specific activity of mitochondrial proteins, phospholipid content of membranes, oxidant and anti-oxidant capacities, oxidative phosphorylation, and calcium retention capacities. Herein we will briefly review the life cycle and functions of mitochondria, the importance of estrogen receptors and the effects of estrogens on heart and skeletal muscle mitochondria.
Keywords: estrogen receptors; estrogens; heart; mitochondria; sexual dimorphism; skeletal muscle.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

