A Robust and Universal Metaproteomics Workflow for Research Studies and Routine Diagnostics Within 24 h Using Phenol Extraction, FASP Digest, and the MetaProteomeAnalyzer
- PMID: 31474963
- PMCID: PMC6707425
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01883
A Robust and Universal Metaproteomics Workflow for Research Studies and Routine Diagnostics Within 24 h Using Phenol Extraction, FASP Digest, and the MetaProteomeAnalyzer
Abstract
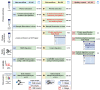
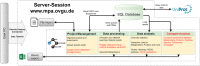
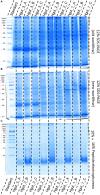
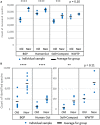
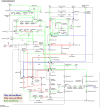
The investigation of microbial proteins by mass spectrometry (metaproteomics) is a key technology for simultaneously assessing the taxonomic composition and the functionality of microbial communities in medical, environmental, and biotechnological applications. We present an improved metaproteomics workflow using an updated sample preparation and a new version of the MetaProteomeAnalyzer software for data analysis. High resolution by multidimensional separation (GeLC, MudPIT) was sacrificed to aim at fast analysis of a broad range of different samples in less than 24 h. The improved workflow generated at least two times as many protein identifications than our previous workflow, and a drastic increase of taxonomic and functional annotations. Improvements of all aspects of the workflow, particularly the speed, are first steps toward potential routine clinical diagnostics (i.e., fecal samples) and analysis of technical and environmental samples. The MetaProteomeAnalyzer is provided to the scientific community as a central remote server solution at www.mpa.ovgu.de.
Keywords: bioinformatics; environmental proteomics; gut microbiome; mass spectrometry; microbial communities; sample preparation; software.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The MetaProteomeAnalyzer: a powerful open-source software suite for metaproteomics data analysis and interpretation.J Proteome Res. 2015 Mar 6;14(3):1557-65. doi: 10.1021/pr501246w. Epub 2015 Feb 23. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 25660940
-
Benchmarking low- and high-throughput protein cleanup and digestion methods for human fecal metaproteomics.mSystems. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):e0066124. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00661-24. Epub 2024 Jun 27. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38934547 Free PMC article.
-
A complete and flexible workflow for metaproteomics data analysis based on MetaProteomeAnalyzer and Prophane.Nat Protoc. 2020 Oct;15(10):3212-3239. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-0368-7. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32859984
-
Challenges and perspectives of metaproteomic data analysis.J Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 10;261:24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.06.1201. Epub 2017 Jun 27. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28663049 Review.
-
Critical steps in an environmental metaproteomics workflow.Environ Microbiol. 2024 May;26(5):e16637. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.16637. Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38760994 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiome Diversity and Community-Level Change Points within Manure-based small Biogas Plants.Microorganisms. 2020 Aug 1;8(8):1169. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081169. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32752188 Free PMC article.
-
Five key aspects of metaproteomics as a tool to understand functional interactions in host-associated microbiomes.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Feb 25;17(2):e1009245. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009245. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33630960 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Metaproteomics in the One Health framework for unraveling microbial effectors in microbiomes.Microbiome. 2025 May 23;13(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s40168-025-02119-5. Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40410872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microbiologist's guide to metaproteomics.Imeta. 2025 May 6;4(3):e70031. doi: 10.1002/imt2.70031. eCollection 2025 Jun. Imeta. 2025. PMID: 40469504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Insights into Bacterial Responses to Antibiotics: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 27;26(15):7255. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157255. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

