Retrograde Ret signaling controls sensory pioneer axon outgrowth
- PMID: 31476133
- PMCID: PMC6718271
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.46092
Retrograde Ret signaling controls sensory pioneer axon outgrowth
Erratum in
-
Correction: Retrograde Ret signaling controls sensory pioneer axon outgrowth.Elife. 2025 Aug 22;14:e108945. doi: 10.7554/eLife.108945. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40843589 Free PMC article.
Abstract
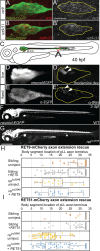
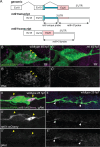
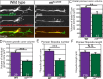
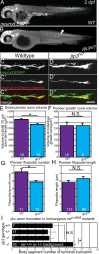
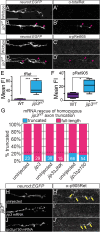
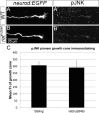
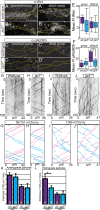
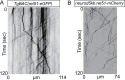
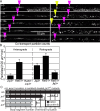
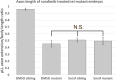
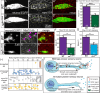
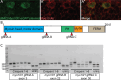
The trafficking mechanisms and transcriptional targets downstream of long-range neurotrophic factor ligand/receptor signaling that promote axon growth are incompletely understood. Zebrafish carrying a null mutation in a neurotrophic factor receptor, Ret, displayed defects in peripheral sensory axon growth cone morphology and dynamics. Ret receptor was highly enriched in sensory pioneer neurons and Ret51 isoform was required for pioneer axon outgrowth. Loss-of-function of a cargo adaptor, Jip3, partially phenocopied Ret axonal defects, led to accumulation of activated Ret in pioneer growth cones, and reduced retrograde Ret51 transport. Jip3 and Ret51 were also retrogradely co-transported, ultimately suggesting Jip3 is a retrograde adapter of active Ret51. Finally, loss of Ret reduced transcription and growth cone localization of Myosin-X, an initiator of filopodial formation. These results show a specific role for Ret51 in pioneer axon growth, and suggest a critical role for long-range retrograde Ret signaling in regulating growth cone dynamics through downstream transcriptional changes.
Keywords: Ret; axon growth; axonal transport; developmental biology; growth cone; lateral line; neuroscience; pioneer neuron; zebrafish.
© 2019, Tuttle et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AT, CD, MM, HM, AN No competing interests declared
Figures


References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics international. 2004;11:36–42.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

