Effects of Antihypertensive Class on Falls, Syncope, and Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adults: The ALLHAT Trial
- PMID: 31476905
- PMCID: PMC6739183
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13445
Effects of Antihypertensive Class on Falls, Syncope, and Orthostatic Hypotension in Older Adults: The ALLHAT Trial
Abstract
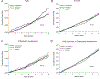
Hypertension treatment has been implicated in falls, syncope, and orthostatic hypotension (OH), common events among older adults. Whether the choice of antihypertensive agent influences the risk of falls, syncope, and OH in older adults is unknown. ALLHAT (Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial) was a randomized clinical trial that compared the effects of hypertension first-step therapy on fatal coronary heart disease or nonfatal myocardial infarction (1994-2002). In a subpopulation of ALLHAT participants, age 65 years and older, we determined the relative risk of falls, syncope, OH, or a composite based on Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and Veterans Affairs claims, using Cox regression. We also determined the adjusted association of self-reported atenolol use (ascertained at the 1-month visit for indications other than hypertension) on outcomes in Cox models adjusted for age, sex, and race. Among 23 964 participants (mean age 69.8±6.8 years, 45% women, 31% non-Hispanic black) followed for a mean of 4.9 years, we identified 267 falls, 755 syncopes, 249 OH, and 1157 composite claims. There were no significant differences in the cumulative incidences of events across randomized drug assignments. However, amlodipine increased risk of falls during the first year of follow-up compared with chlorthalidone (hazard ratio [95% CI]: 2.24 [1.06-4.74]; P=0.03) or lisinopril (hazard ratio [95% CI]: 2.61 [1.03-6.72]; P=0.04). Atenolol use (N=928) was not associated with any of the 3 individual or composite claims. In older adults, the choice of antihypertensive agent had no effect on risk of fall, syncope, or OH long-term. However, amlodipine increased risk of falls within 1 year of initiation. These short-term findings require confirmation. Clinical Trial Registration- URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00000542.
Keywords: amlodipine; chlorthalidone; fall; lisinopril; orthostatic hypotension; syncope.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R, Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360:1903–1913. - PubMed
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA. 2002;288:2981–2997. - PubMed
-
- Puttnam R, Davis BR, Pressel SL, Whelton PK, Cushman WC, Louis GT, Margolis KL, Oparil S, Williamson J, Ghosh A, Einhorn PT, Barzilay JI, Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) Collaborative Research Group. Association of 3 Different Antihypertensive Medications With Hip and Pelvic Fracture Risk in Older Adults: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Heseltine D, Bramble MG. Loop diuretics cause less postural hypotension than thiazide diuretics in the frail elderly. Curr Med Res Opin. 1988;11:232–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

