Unique α-synuclein pathology within the amygdala in Lewy body dementia: implications for disease initiation and progression
- PMID: 31477175
- PMCID: PMC6718048
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-019-0787-2
Unique α-synuclein pathology within the amygdala in Lewy body dementia: implications for disease initiation and progression
Abstract
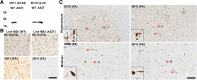
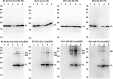
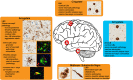
The protein α-synuclein (αsyn) forms pathologic aggregates in a number of neurodegenerative diseases including Lewy body dementia (LBD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). It is unclear why diseases such as LBD may develop widespread αsyn pathology, while in Alzheimer's disease with amygdala restricted Lewy bodies (AD/ALB) the αsyn aggregates remain localized. The amygdala contains αsyn aggregates in both LBD and in AD/ALB; to understand why αsyn pathology continues to progress in LBD but not in AD/ALB, tissue from the amygdala and other regions were obtained from 14 cases of LBD, 9 cases of AD/ALB, and 4 controls for immunohistochemical and biochemical characterization. Utilizing a panel of previously characterized αsyn antibodies, numerous unique pathologies differentiating LBD and AD/ALB were revealed; particularly the presence of dense neuropil αsyn aggregates, astrocytic αsyn, and αsyn-containing dystrophic neurites within senile plaques. Within LBD, these unique pathologies were predominantly present within the amygdala. Biochemically, the amygdala in LBD prominently contained specific carboxy-truncated forms of αsyn which are highly prone to aggregate, suggesting that the amygdala may be prone to initiate development of αsyn pathology. Similar to carboxy-truncated αsyn, it was demonstrated herein that the presence of aggregation prone A53T αsyn is sufficient to drive misfolding of wild-type αsyn in human disease. Overall, this study identifies within the amygdala in LBD the presence of unique strain-like variation in αsyn pathology that may be a determinant of disease progression.
Keywords: Amygdala; Astrocyte; Inclusion formation; Lewy body; Lewy body dementia; Neurodegeneration; Parkinson’s disease; Truncation; α-Synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Abdelmotilib H, Maltbie T, Delic V, Liu Z, Hu X, Fraser KB, Moehle MS, Stoyka L, Anabtawi N, Krendelchtchikova V, Volpicelli-Daley LA, West A. α-Synuclein fibril-induced inclusion spread in rats and mice correlates with dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;105:84–98. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.05.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, Diep L, Keim PS, Shen X, Chataway T, Schlossmacher MG, Seubert P, Schenk D, Sinha S, Gai WP, Chilcote TJ. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of α-Synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:29739–29752. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600933200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beach TG, White CL, Hamilton RL, Duda JE, Iwatsubo T, Dickson DW, Leverenz JB, Roncaroli F, Buttini M, Hladik CL, Sue LI, Noorigian JV, Adler CH. Evaluation of α-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;116:277–288. doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0409-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

