Optimization of cell suspension culture of transformed and untransformed lettuce for the enhanced production of secondary metabolites and their pharmaceutical evaluation
- PMID: 31478032
- PMCID: PMC6704210
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1870-x
Optimization of cell suspension culture of transformed and untransformed lettuce for the enhanced production of secondary metabolites and their pharmaceutical evaluation
Abstract
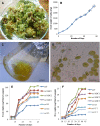
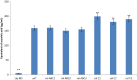
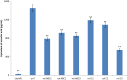
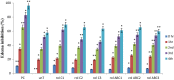
In vitro suspension culture techniques are cost effective for large-scale production of secondary metabolites. In the present study, firstly, suspension cultures of untransformed Lactuca sativa were prepared using different hormonal combinations and were subjected to different pH, temperature and salt concentrations. Maximum biomass was obtained for suspensions supplemented with 1.5 mg/L BAP and 0.1 mg/L NAA, at pH 5.8, temperature 28 °C and 0 mM NaCl concentration. Using these parameters, suspensions were produced for rol ABC- and rol C-transformed lines of L. sativa. All the transgenic lines showed prominent increase in fresh weight (FW) and dry weight (DW) with maximum values for rol ABC2 line producing 169.8 mg/mL FW and 25.3 mg/mL DW. The exudates of transformed and untransformed plants were tested for the antioxidant activity and in vivo assays on rats. Maximum phenolic content (261 μg/mL) and flavonoid content (637.6 μg/mL) were obtained for rol C1 transgenic line. Total antioxidant capacity was found maximum (1451.7 μg/mL) for untransformed lettuce, whereas rol C1 showed maximum total reducing power activity (637.6 μg/mL). In DPPH assay, maximum activity (104.7 μg/mL) was shown by rol ABC3 line. In rats analgesic assay, maximum activity (74.9%) was shown by rol C2. Line rol C1 showed maximum anti-inflammatory activity (69.2%) and maximum antidepressant activity (minimum immobility time of 55 s). Maximum anticoagulant activity was observed for rol ABC2 with maximum clotting time of 130 s. The present study could help in using lettuce suspension culture as platform for the enhanced production of important metabolites.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Cell suspension; Lactuca sativa; Rats; Rol genes; Transgenic plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe author declares that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Al-Maskri A, Al-Kharusi L, Al-Miqbali H, Khan MM. Effects of salinity stress on growth of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) under closed-recycle nutrient film technique. Int J Agri Biol. 2010;12(3):377–380.
-
- Araruna K, Carlos B. Anti-inflammatory activities of triterpene lactones from Lactuca sativa. Phytopharmacology. 2010;1(1):1–6.
-
- Asif (2013) Optimization of tissue culture and transformation Conditions of Selected Edible Plant Species (Thesis). Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabd
-
- Balandrin MF, Klocke JA. Medicinal, aromatic and industrial materials from plants. In: Bajaj YPS, editor. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry. Berlin: Springer; 1988. pp. 1–35.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

