Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people
- PMID: 31478559
- PMCID: PMC6719256
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub4
Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people
Abstract
Background: This is an update of the original review published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Issue 10, 2015.Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is the most common life-threatening opportunistic invasive mould infection in immunocompromised people. Early diagnosis of IA and prompt administration of appropriate antifungal treatment are critical to the survival of people with IA. Antifungal drugs can be given as prophylaxis or empirical therapy, instigated on the basis of a diagnostic strategy (the pre-emptive approach) or for treating established disease. Consequently, there is an urgent need for research into both new diagnostic tools and drug treatment strategies. Increasingly, newer methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect fungal nucleic acids are being investigated.
Objectives: To provide an overall summary of the diagnostic accuracy of PCR-based tests on blood specimens for the diagnosis of IA in immunocompromised people.
Search methods: We searched MEDLINE (1946 to June 2015) and Embase (1980 to June 2015). We also searched LILACS, DARE, Health Technology Assessment, Web of Science and Scopus to June 2015. We checked the reference lists of all the studies identified by the above methods and contacted relevant authors and researchers in the field. For this review update we updated electronic searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2018, Issue 3) in the Cochrane Library; MEDLINE via Ovid (June 2015 to March week 2 2018); and Embase via Ovid (June 2015 to 2018 week 12).
Selection criteria: We included studies that: i) compared the results of blood PCR tests with the reference standard published by the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG); ii) reported data on false-positive, true-positive, false-negative and true-negative results of the diagnostic tests under investigation separately; and iii) evaluated the test(s) prospectively in cohorts of people from a relevant clinical population, defined as a group of individuals at high risk for invasive aspergillosis. Case-control and retrospective studies were excluded from the analysis.
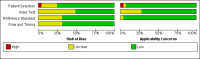
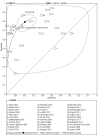
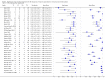
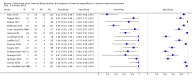
Data collection and analysis: Authors independently assessed quality and extracted data. For PCR assays, we evaluated the requirement for either one or two consecutive samples to be positive for diagnostic accuracy. We investigated heterogeneity by subgroup analyses. We plotted estimates of sensitivity and specificity from each study in receiver operating characteristics (ROC) space and constructed forest plots for visual examination of variation in test accuracy. We performed meta-analyses using the bivariate model to produce summary estimates of sensitivity and specificity.
Main results: We included 29 primary studies (18 from the original review and 11 from this update), corresponding to 34 data sets, published between 2000 and 2018 in the meta-analyses, with a mean prevalence of proven or probable IA of 16.3 (median prevalence 11.1% , range 2.5% to 57.1%). Most patients had received chemotherapy for haematological malignancy or had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Several PCR techniques were used among the included studies. The sensitivity and specificity of PCR for the diagnosis of IA varied according to the interpretative criteria used to define a test as positive. The summary estimates of sensitivity and specificity were 79.2% (95% confidence interval (CI) 71.0 to 85.5) and 79.6% (95% CI 69.9 to 86.6) for a single positive test result, and 59.6% (95% CI 40.7 to 76.0) and 95.1% (95% CI 87.0 to 98.2) for two consecutive positive test results.
Authors' conclusions: PCR shows moderate diagnostic accuracy when used as screening tests for IA in high-risk patient groups. Importantly the sensitivity of the test confers a high negative predictive value (NPV) such that a negative test allows the diagnosis to be excluded. Consecutive positives show good specificity in diagnosis of IA and could be used to trigger radiological and other investigations or for pre-emptive therapy in the absence of specific radiological signs when the clinical suspicion of infection is high. When a single PCR positive test is used as the diagnostic criterion for IA in a population of 100 people with a disease prevalence of 16.3% (overall mean prevalence), three people with IA would be missed (sensitivity 79.2%, 20.8% false negatives), and 17 people would be unnecessarily treated or referred for further tests (specificity of 79.6%, 21.4% false positives). If we use the two positive test requirement in a population with the same disease prevalence, it would mean that nine IA people would be missed (sensitivity 59.6%, 40.4% false negatives) and four people would be unnecessarily treated or referred for further tests (specificity of 95.1%, 4.9% false positives). Like galactomannan, PCR has good NPV for excluding disease, but the low prevalence of disease limits the ability to rule in a diagnosis. As these biomarkers detect different markers of disease, combining them is likely to prove more useful.
Conflict of interest statement
RAB has been a consultant to Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Sharpe & Dohme, Pfizer and Schering‐Plough, has received a research grant from Pfizer, has been a member of a speakers' bureau for Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Sharpe & Dohme, Pfizer and Schering‐Plough, and has received travel grants from Astellas Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Sharpe & Dohme, Pfizer and Schering‐Plough.
JL has received research grants from Novartis and travel grants from Pfizer and Cephalon.
PD has been a consultant to Gilead Sciences, Ipsat Therapies and Pfizer, has received research grants from AM‐Pharma, Basilea Pharmaceutica and Schering‐Plough, has been a member of a speakers' bureau for Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Schering‐Plough, and Xian‐Janssen and has received travel grants from Merck, Sharpe & Dohme and UCB Pharma.
LK has been an adviser to Astellas, Gilead, Schering‐Plough, has received research grants from Gilead, Merck, Sharpe & Dohme, Schering‐Plough and has received honoraria for educational lectures from Gilead, Pfizer, Merck, Sharpe & Dohme, Schering‐Plough and Janssen.
BLJ has been an advisor to Gilead, MSD, Astellas and Pfizer; has received research grants from Gilead, Astellas, Pfizer, Janssen and MSD; has received honoraria for educational lectures from Gilead, MSD and Pfizer; and owns stock in Gilead, MSD and Pfizer.
JM has served as consultant to Schering‐Plough, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Bio‐Rad, Fujisawa healthcare, Astellas, Nextar and Zeneus (Cephalon), has received research funding from Bio‐Rad, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, and has been on the speakers' bureau for Schering‐Plough, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Bio‐Rad, Fujisawa healthcare, Astellas and Zeneus (Cephalon).
MC, CM, OM: no conflicts of interest to declare with regard to the content of the article.
LW has received research funding from Bruker, Luminex and Renishaw Diagnostics, provided consultancy for Gilead Sciences, has been a member of a speakers' bureau for Gilead Sciences, Merck, Sharpe and Dohme, Bruker and Dynamiker Ltd, and received travels funding from Gilead Sciences, Launch Diagnostics, Bruker and Renishaw Diagnostics.
RAB, JL and PD are founder members of the European
None of the authors has any interests, financial or otherwise, in any of the companies involved in the diagnosis of IFD. The authors' disclosures are on public record to ensure their independence and integrity and to help avoid potential conflicts of interest.
Figures












Update of
-
Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 7;(9):CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 01;(10):CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub3. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 03;9:CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub4. PMID: 26343815 Updated.
Similar articles
-
Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 1;(10):CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26424726
-
Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 7;(9):CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 01;(10):CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub3. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 03;9:CD009551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009551.pub4. PMID: 26343815 Updated.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 24;3(3):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7:CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. PMID: 33760236 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Galactomannan detection in broncho-alveolar lavage fluid for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 20;5(5):CD012399. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012399.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31107543 Free PMC article.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Outbreaks of Fungal Infections in Hospitals: Epidemiology, Detection, and Management.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Oct 29;9(11):1059. doi: 10.3390/jof9111059. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;9(2):131. doi: 10.3390/jof9020131. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recognition of Diagnostic Gaps for Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases: Expert Opinion from the Fungal Diagnostics Laboratories Consortium (FDLC).J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Jun 18;59(7):e0178420. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01784-20. Epub 2021 Jun 18. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33504591 Free PMC article.
-
[S1 guideline: diagnosis and treatment of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill/intensive care patients].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2025 May;120(4):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s00063-025-01265-w. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2025. PMID: 40116920 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
An Overview of Systematic Reviews of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for the Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis in Immunocompromised People: A Report of the Fungal PCR Initiative (FPCRI)-An ISHAM Working Group.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Sep 26;9(10):967. doi: 10.3390/jof9100967. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37888223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aslan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Aslan M, Oz Y, Aksit F, Akay OM. Potential of polymerase chain reaction and galactomannan for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with febrile neutropenia. Mycoses 2015;58(6):343‐9. - PubMed
Badiee 2010 {published data only}
-
- Badiee P, Alborzi A. Detection of Aspergillus species in bone marrow transplant patients. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 2010;4(8):511‐6. - PubMed
Badiee 2017 {published data only}
-
- Badiee P, Zareifar S, Haddadi P, Jafarian H. Incidence of fungal infections in pediatric patients with hematologic neoplasms. Archives of Pediatric Infectious Diseases 2017;5(3):e41317.
Barnes 2009 {published data only}
-
- Barnes RA, White PL, Bygrave C, Evans N, Healy B, Kell J. Clinical impact of enhanced diagnosis of invasive fungal disease in high‐risk haematology and stem cell transplant patients. Journal of Clinical Pathology 2009;62(1):64‐9. - PubMed
Barnes 2013 {published data only}
-
- Barnes RA, Stocking K, Bowden S, Poynton MH, White PL. Prevention and diagnosis of invasive fungal disease in high‐risk patients within an integrative care pathway. Journal of Infection 2013;67(3):206‐14. - PubMed
Bellanger 2015 {published data only}
-
- Bellanger AP, Millon L, Berceanu A, Grenouillet F, Grenouillet FE, Larosa F, et al. Combining Aspergillus mitochondrial and ribosomal QPCR, in addition to galactomannan assay, for early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in hematology patients. Medical Mycology 2015;53(7):760‐4. - PubMed
Boch 2016 {published data only}
-
- Boch T, Spiess B, Cornely OA, Vehreschild JJ, Rath PM, Steinmann J, et al. Diagnosis of invasive fungal infections in haematological patients by combined use of galactomannan, 1,3‐beta‐D‐glucan, Aspergillus PCR, multifungal DNA‐microarray, and Aspergillus azole resistance PCRs in blood and bronchoalveolar lavage samples: results of a prospective multicentre study. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2016;22(10):862‐8. - PubMed
Boluk 2016 {published data only}
-
- Boluk G, Kazak E, Ozkalemkas F, Ener B, Akalin H, Agca H. Comparison of galactomannan, beta‐d‐glucan, and aspergillus DNA in sera of high‐risk adult patients with hematological malignancies for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2016;46(2):335‐42. - PubMed
Cuenca‐Estrella 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cuenca‐Estrella M, Meije Y, Diaz‐Pedroche C, Gomez‐Lopez A, Buitrago M‐J, Bernal‐Martinez L, et al. Value of serial quantification of fungal DNA by a real‐time PCR‐based technique for early diagnosis of invasive Aspergillosis in patients with febrile neutropenia. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2009;47(2):379‐84. - PMC - PubMed
da Silva 2010 {published data only}
El Mahallawy 2006 {published data only}
-
- El‐Mahallawy HA, Shaker HH, Ali Helmy H, Mostafa T, Abo‐Sedah AR. Evaluation of pan‐fungal PCR assay and Aspergillus antigen detection in the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections in high risk paediatric cancer patients. Medical Mycology 2006;44:733‐9. - PubMed
Ferns 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ferns B, Fletcher H, Bradley S, Mackinnon S, Hunt C, Tedder RS. The prospective evaluation of a nested polymerase chain reaction assay for the early detection of Aspergillus infection in patients with leukaemia or undergoing allograft treatment. British Journal of Haematology 2002;119(3):720‐5. - PubMed
Florent 2006 {published data only}
-
- Florent M, Katsahian S, Vekhoff A, Levy V, Rio B, Marie JP, et al. Prospective evaluation of a polymerase chain reaction‐ELISA targeted to Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus for the early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematological malignancies. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2006;193(5):741‐7. - PubMed
Halliday 2006 {published data only}
-
- Halliday C, Hoile R, Sorrell T, James G, Yadav S, Shaw P, et al. Role of prospective screening of blood for invasive aspergillosis by polymerase chain reaction in febrile neutropenic recipients of haematopoietic stem cell transplants and patients with acute leukaemia. British Journal of Haematology 2006;132(4):478‐86. - PubMed
Hebart 2000a {published data only}
-
- Hebart H, Loffler J, Reitze H, Engel A, Schumacher U, Klingebiel T, et al. Prospective screening by a panfungal polymerase chain reaction assay in patients at risk for fungal infections: implications for the management of febrile neutropenia. British Journal of Haematology 2000;111(2):635‐40. - PubMed
Hummel 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hummel M, Spiess B, Roder J, Komorowski G, Durken M, Kentouche K, et al. Detection of Aspergillus DNA by a nested PCR assay is able to improve the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in paediatric patients. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2009;58(Pt 10):1291‐7. - PubMed
Imbert 2016 {published data only}
Landlinger 2010 {published data only}
-
- Landlinger C, Preuner S, Baskova L, Grotel M, Hartwig NG, Dworzak M, et al. Diagnosis of invasive fungal infections by a real‐time panfungal PCR assay in immunocompromised pediatric patients. Leukemia 2010;24(12):2032‐8. - PubMed
Loeffler 2017 {published data only}
Pini 2015 {published data only}
-
- Pini P, Bettua C, Orsi CF, Venturelli C, Faglioni L, Forghieri F, et al. Clinical performance of a commercial real‐time PCR assay for Aspergillus DNA detection in serum samples from high‐risk patients: comparison with a galactomannan enzyme immunoassay. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2015;34(1):131‐6. - PubMed
Ramírez 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ramírez M, Castro C, Palomares JC, Torres MJ, Aller AI, Ruiz M, et al. Molecular detection and identification of Aspergillus spp. from clinical samples using real‐time PCR. Mycoses 2009;52(2):129‐34. - PubMed
Rogers 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rogers TR, Morton CO, Springer J, Conneally E, Heinz W, Kenny C, et al. Combined real‐time PCR and galactomannan surveillance improves diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in high risk patients with haematological malignancies. British Journal of Haematology 2013;161(4):517‐24. - PubMed
Schwarzinger 2013 {published data only}
Springer 2011 {published data only}
Springer 2016 {published data only}
-
- Springer J, Lackner M, Nachbaur D, Girschikofsky M, Risslegger B, Mutschlechner W, et al. Prospective multicentre PCR‐based Aspergillus DNA screening in high‐risk patients with and without primary antifungal mould prophylaxis. Clinical microbiology and infection 2016;22:80‐86. - PubMed
Suarez 2008 {published data only}
-
- Suarez F, Lortholary O, Buland S, Rubio MT, Ghez D, Mahe V, et al. Detection of circulating Aspergillus fumigatus DNA by real‐time PCR assay of large serum volumes improves early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in high‐risk adult patients under hematologic surveillance. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2008;46(11):3772‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Sugawara 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sugawara Y, Nakase K, Nakamura A, Ohishi K, Sugimoto Y, Fujieda A, et al. Clinical utility of a panfungal polymerase chain reaction assay for invasive fungal diseases in patients with haematologic disorders. European Journal of Haematology 2013;90(4):331‐9. - PubMed
von Lilienfeld‐Toal 2009 {published data only}
White 2006 {published data only}
-
- White PL, Linton CJ, Perry MD, Johnson EM, Barnes RA. The evolution and evaluation of a PCR assay for the detection of invasive aspergillosis in haematology patients. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006;42(4):479‐86. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adhurti 2011 {published data only}
-
- Adurthi S, Sahoo TP, Shafiulla M, Radhika B, Jacob LA, Appaji L, et al. Invasive fungal infections in haematological malignancies at a regional cancer institute‐role of panfungal PCR. European Journal of Cancer Supplements 2011;9(1):18.
Aguado 2015 {published data only}
-
- Aguado JM, Vazquez L, Fernandez‐Ruiz M. Serum galactomannan versus a combination of galactomannan and polymerase chain reaction‐based aspergillus DNA detection for early therapy of invasive aspergillosis in high‐risk hematological patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2015;60(3):405‐14. - PubMed
Armenian 2009 {published data only}
-
- Armenian SH, Nash KA, Kapoor N, Franklin JL, Gaynon PS, Ross LA, et al. Prospective monitoring for invasive aspergillosis using galactomannan and polymerase chain reaction in high risk pediatric patients. Journal of Pediatric Hematology/oncology 2009;31(12):920‐6. - PubMed
Auberger 2011 {published data only}
-
- Auberger J, Clausen J, Mrazek C, Lass‐Florl C, Nachbaur D. Breakthrough fungal infections (bIFI), fungal colonization and emergence of resistant strains during posaconazole (PCZ) prophylaxis in patients at risk. Real‐life data from a single center institutional retrospective observational study. Onkologie 2011;34:232. - PubMed
Badiee 2008 {published data only}
-
- Badiee P, Kordbacheh P, Alborzi A, Ramzi M, Shakiba E. Molecular detection of invasive aspergillosis in hematologic malignancies. Infection 2008;36(6):580‐4. - PubMed
Badiee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Badiee P, Kordbacheh P, Alborzi A, Malekhoseini S, Ramzi M, Mirhendi H, et al. Study on invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients to present a suitable early diagnostic procedure. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2009;13(1):97‐102. - PubMed
Badiee 2016a {published data only}
Badiee 2016b {published data only}
-
- Badiee P, Moghadami M, Rozbehani H. Comparing immunological and molecular tests with conventional methods in diagnosis of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 2016;10(1):90‐5. - PubMed
Bernal‐Martinez 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bernal‐Martinez L, Gago S, Buitrago MJ, Gomez‐Lopez A, Rodriguez‐Tudela JL, Cuenca‐Estrella M. Analysis of performance of a PCR‐based assay to detect DNA of Aspergillus fumigatus in whole blood and serum: a comparative study with clinical samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2011;49(10):3596‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Blennow 2010 {published data only}
-
- Blennow O, Remberger M, Klingspor L, Omazic B, Fransson K, Ljungman P, et al. Randomized PCR‐based therapy and risk factors for invasive fungal infection following reduced‐intensity conditioning and hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplantation 2010;45(12):1710‐8. - PubMed
Boch 2015 {published data only}
-
- Boch T, Reinwald M, Postina P, Cornely OA, Vehreschild JJ, Heusel CP, et al. Identification of invasive fungal diseases in immunocompromised patients by combining an Aspergillus specific PCR with a multifungal DNA‐microarray from primary clinical samples. Mycoses 2015;58(12):735‐45. - PubMed
Bolehovska 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bolehovska R, Pliskova L, Buchta V, Cerman J, Hamal P. Detection of Aspergillus spp. in biological samples by real‐time PCR. Biomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czechoslovakia 2006;150(2):245‐8. - PubMed
Bretagne 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bretagne S, Costa JM, Bart‐Delabesse E, Dhedin N, Rieux C, Cordonnier C. Comparison of serum galactomannan antigen detection and competitive polymerase chain reaction for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1998;26(6):1407‐12. - PubMed
Bucheidt 2001 {published data only}
-
- Buchheidt D, Baust C, Skladny H, Ritter J, Suedhoff T, Baldus M, et al. Detection of Aspergillus species in blood and bronchoalveolar lavage samples from immunocompromised patients by means of 2‐step polymerase chain reaction: clinical results. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2001;33(4):428‐35. - PubMed
Bucheidt 2004 {published data only}
-
- Buchheidt D, Hummel M, Schleiermacher D, Spiess B, Schwerdtfeger R, Cornely OA, et al. British Journal of Haematology 2004; 125:196‐202. - PubMed
Bu Rong 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bu R, Sathiapalan RK, Ibrahim MM, Al‐Mohsen I, Almodavar E, Gutierrez MI, et al. Monochrome LightCycler PCR assay for detection and quantification of five common species of Candida and Aspergillus. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2005;54(Pt 3):243‐8. - PubMed
Capoor 2017 {published data only}
-
- Capoor MR, Puri S, Raheja H, Mohindra R, Gupta DK, Verma PK, et al. Screening of invasive fungal infections by a real‐time panfungal (pan‐ACF) polymerase chain reaction assay in patients with haematological malignancy. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology 2017;35(1):41‐7. - PubMed
Cesaro 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cesaro S, Stenghele C, Calore E, Franchin E, Cerbaro I, Cusinato R, et al. Assessment of the LightCycler PCR assay for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in paediatric patients with onco‐haematological diseases. Mycoses 2008;51(6):497‐504. - PubMed
Challier 2004 {published data only}
Chryssanthou 1999 {published data only}
-
- Chryssanthou E, Klingspor L, Tollemar J, Petrini B, Larsson L, Christensson B, et al. PCR and other non‐culture methods for diagnosis of invasive Candida infections in allogeneic bone marrow and solid organ transplant recipients. Mycoses 1999;42(4):239‐47. - PubMed
Danylo 2014 {published data only}
-
- Danylo A, Courtemanche C, Pelletier R, Boudreault AA. Performance of MycAssay Aspergillus DNA real‐time PCR assay compared with the galactomannan detection assay for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis from serum samples. Medical Mycology 2014;52(6):577‐83. - PubMed
da Silva 2014 {published data only}
-
- Silva TV, Carneiro LC, Ramos Fdos S. PCR as a screening test for invasive aspergillosis in haematological patients: a pilot study. Mycopathologia 2014;177(1‐2):111‐4. - PubMed
Drogari‐Apiranthitou 2016 {published data only}
-
- Drogari‐Apiranthitou M, Panayiotides I, Galani I, Konstantoudakis S, Arvanitidis G, Spathis, A, et al. Diagnostic value of a semi‐nested PCR for the diagnosis of mucormycosis and aspergillosis from paraffin‐embedded tissue: a single center experience. Pathology, Research and Practice 2016;212(5):393‐7. - PubMed
Du 2016 {published data only}
Gupta 2017 {published data only}
-
- Gupta P, Ahmad A, Khare V, Kumar A, Banerjee G, Verma N, et al. Comparative evaluation of pan‐fungal real‐time PCR, galactomannan and (1‐3)‐beta‐D‐glucan assay for invasive fungal infection in paediatric cancer patients. Mycoses 2017;60(4):234‐40. - PubMed
Hadrich 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hadrich I, Mary C, Makni F, Elloumi M, Dumon H, Ayadi A, et al. Comparison of PCR‐ELISA and Real‐Time PCR for invasive aspergillosis diagnosis in patients with hematological malignancies.. Medical Mycology 2011;49:489‐94. - PubMed
Halliday 2005 {published data only}
Hasseine 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hasseine L, Marty P, Cassaing S, Robert‐Gangneux F, Gaudron L, Knecht R, et al. Multicentre prospective monitoring for empirical treatment of invasive fungal infection using high negative predictive value diagnostic strategies. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2010;16:S207‐8.
Hebart 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hebart H, Löffler J, Meisner C, Serey F, Schmidt D, Böhme A, et al. Early detection of aspergillus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation by polymerase chain reaction screening. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000;181(5):1713‐9. - PubMed
Hummel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hummel M, Spiess B, Cornely OA, Dittmer M, Mörz H, Buchheidt D. Aspergillus PCR testing: results from a prospective PCR study within the AmBiLoad trial. European Journal of Haematology 2010;85(2):164‐9. - PubMed
Idelevich 2015 {published data only}
-
- Idelevich EA, Silling G, Niederbracht Y, Penner H, Sauerland MC, Tafelski S, et al. Impact of multiplex PCR on antimicrobial treatment in febrile neutropenia: a randomized controlled study. Medical Microbiology and Immunology 2015;204(5):585‐92. - PubMed
Johnson 2012 {published data only}
Jones 1998 {published data only}
Jordanides 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jordanides NE, Allan EK, McLintock LA, Copland M, Devaney M, Stewart K, et al. A prospective study of real‐time panfungal PCR for the early diagnosis of invasive fungal infection in haemato‐oncology patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005;35(4):389‐95. - PubMed
Kalkank 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kalkanc A, Aki SZ, Yegin ZA, Suyan E, Tuncca O, Koktur N, et al. Molecular approaches to fungal infections in high‐risk haematology patients. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2010;16:S229.
Kami 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kami M, Fukui T, Ogawa S, Kazuyama Y, Machida U, Tanaka Y, et al. Use of real‐time PCR on blood samples for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2001;33(9):1504‐12. - PubMed
Kawazu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kawazu M, Kanda Y, Nannya Y, Aoki K, Kurokawa M, Chiba S, et al. Prospective comparison of the diagnostic potential of real‐time PCR, double‐sandwich enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay for galactomannan, and a (1‐‐>3)‐beta‐D‐glucan test in weekly screening for invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematological disorders. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2004;42(6):2733‐41. - PMC - PubMed
Khalid 2017 {published data only}
-
- Khalid A, Chua AL, Tzar MN, Santhanam J. development of prototype multiplexed lateral flow assay (LFA) for rapid detection of invasive fungal infections. Medical journal of Malaysia. 2017; Vol. 72 (supplement 2):24.
Klingspor 2006 {published data only}
-
- Klingspor L, Jalal S. Molecular detection and identification of Candida and Aspergillus spp. from clinical samples using real‐time PCR. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2006;12(8):745‐53. - PubMed
Lass‐Florl 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lass‐Florl C, Aigner J, Gunsilius E, Petzer A, Nachbaur D, Gastl G, et al. Screening for Aspergillus spp. using polymerase chain reaction of whole blood samples from patients with haematological malignancies. British Journal of Haematology 2001;113(1):180‐4. - PubMed
Lehrnbecher 2016 {published data only}
-
- Lehrnbecher T, Robinson PD, Fisher BT, Castagnola E, Groll AH, Steinbach WJ, et al. Galactomannan, beta‐D‐glucan, and polymerase chain reaction‐based assays for the diagnosis of invasive fungal disease in pediatric cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2016;63(10):1340‐8. - PubMed
Li 2013 {published data only}
Liu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Liu JQ, Feng LM, Song H, Meng HT, Jin J, Qian WB. [Detection of Aspergillus infection in blood of malignant hematopoietic tumor patients by two‐step polymerase chain reaction]. Zhonghua nei ke za zhi [Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine] 2005;44:726‐9. - PubMed
MacEsic 2017 {published data only}
-
- MacEsic N, Morrissey CO, Liew D, Bohensky MA, Chen SC‐A, Gilroy NM, et al. Is a biomarker‐based diagnostic strategy for invasive aspergillosis cost effective in high‐risk haematology patients?. Medical Mycology 2017;55(7):705‐12. - PubMed
Mandhanija 2010 {published data only}
Millon 2011 {published data only}
Morrissey 2013 {published data only}
-
- Morrissey CO, Chen SC, Sorrell TC, Milliken S, Bardy PG, Bradstock KF, et al. Australasian Leukaemia Lymphoma Group and the Australia and New Zealand Mycology Interest Group. Galactomannan and PCR versus culture and histology for directing use of antifungal treatment for invasive aspergillosis in high‐risk haematology patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2013;13(6):519‐28. - PubMed
Nakamura 2010 {published data only}
Oz 2016 {published data only}
-
- Oz Y, Aslan M, Aksit F, Metintas S, Gunduz E. The effect of clinical characteristics on the performance of galactomannan and PCR for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in febrile neutropenic patients. Mycoses 2016;59(2):86‐92. - PubMed
Paholcseck 2015 {published data only}
Paolucci 2013 {published data only}
-
- Paolucci M, Stanzani M, Melchionda F, Tolomelli G, Castellani G, Landini MP, et al. Routine use of a real‐time polymerase chain reaction method for detection of bloodstream infections in neutropaenic patients. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2013;75(2):130‐4. - PubMed
Reinwald 2014 {published data only}
-
- Reinwald M, Konietzka CA, Kolve H. Assessment of Aspergillus‐specific PCR as a screening method for invasive aspergillosis in paediatric cancer patients and allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell recipients with suspected infections. Mycoses 2014;57(9):537‐43. - PubMed
Scotter 2005 {published data only}
-
- Scotter JM, Campbell P, Anderson TP, Murdoch DR, Chambers ST, Patton NW. Comparison of PCR‐ELISA and galactomannan detection for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Pathology 2005;37(3):246‐53. - PubMed
Skladny 1999 {published data only}
Sonmez 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sonmez A, Eksi F, Pehlivan M, Haydaroglu Sahin H. Investigating the presence of fungal agents in febrile neutropenic patients using different microbiological, serological, and molecular methods. Udruzenje Basicnih Mediciniskih Znanosti [Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences] 2015;15(3):40‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Springer 2013 {published data only}
Sun 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sun Y, Ji Y, Xu L, Liu D, Liu K, Huang X. [Combination of real‐time polymerase chain reaction assay and serum galactomannan in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematological malignancies and recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation]. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 2010;90:375‐8. - PubMed
Tang 2016 {published data only}
Teifoori 2011 {published data only}
-
- Teifoori F, Rodbar MS, Sharifi Z, Ghaffari H. Detection of Aspergilus DNA, by a Nested PCR assay and molecula study of Aspergillus fumigatus, by PCR amplification of IGS Region in BMT patients. Mycoses 2011;54:87.
White 2013 {published data only}
Yoo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yoo J, Choi J, Choi S, Lee D, Shin W, Min W, et al. Application of nucleic acid sequence‐based amplification for diagnosis of and monitoring the clinical course of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic diseases. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005;40(3):392‐8. - PubMed
Zhang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zhang S, Wang S, Wan Z, Que C, Li R, Yu J. Quantitative real‐time PCR and platelia galactomannan assay for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid performs better than serum in non‐neutropaenic patients. Mycopathologia 2016;181(9‐10):625‐9. - PubMed
Zhao 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zhao Y, Paderu P, Railkar R, Douglas C, Iannone R, Shire N, et al. Blood Aspergillus RNA is a promising alternative biomarker for invasive aspergillosis. Medical Mycology 2016;54(8):801‐7. - PubMed
Additional references
Arvanitis 2014
Ascioglou 2002
-
- Ascioglu S, Rex JH, Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F, et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2002;34(1):7‐14. - PubMed
Barnes 2018
-
- Barnes RA, White PL, Morton CO, Rogers TR, Cruciani M, Loeffler J, et al. Diagnosis of aspergillosis by PCR: Clinical considerations and technical tips. Medical Mycology 2018;56(suppl.1):60‐72. - PubMed
Baskova 2007
-
- Baskova LC, Landlinger S, Preuner T, Lion T. The Pan‐AC assay: a single‐reaction real‐time PCR test for quantitative detection of a broad range of Aspergillus and Candida species. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2007;56(Pt 9):1167‐73. - PubMed
Bossuyt 2003
-
- Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, et al. Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: the STARD initiative. AJR: American Journal of Roentgenology 2003;181(1):51‐5. - PubMed
Botterel 2008
-
- Botterel F, Farrugia C, Ichai P, Costa JM, Saliba F, Bretagne S. Real‐time PCR on the first galactomannan‐positive serum sample for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis in liver transplant recipients. Transplant Infectious Disease 2008;10(5):333‐8. - PubMed
Bustin 2009
-
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real‐time PCR experiments. Clinical Chemistry 2009;55(4):611‐22. - PubMed
Caillot 2001
-
- Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Bernard A, Casasnovas O, Denning DW, Mannone L, et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2001;19(1):253–9. - PubMed
Chamilos 2006
-
- Chamilos G, Kontoyannis DP. Defining the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Medical Mycology 2006;44(Supplement_1):S163‐73. - PubMed
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta‐analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331‐2. - PubMed
Costa 2001
-
- Costa C, Vidaud D, Olivi M, Bart‐Delabesse E, VidaudM, Bretagne S. Development of two real‐time quantitative TaqMan PCR assays to detect circulating Aspergillus fumigatus DNA in serum. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2001;44(3):263‐9. - PubMed
Covidence 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. Version Accessed prior to 24 July 2019. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation, 2014.
De Pauw 2008
-
- Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;46(12):1813‐21. - PMC - PubMed
Donnelly 2006
-
- Donnelly JP. Polymerase chain reaction for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis: getting closer but still a ways to go. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006;42(4):487‐9. - PubMed
Einsele 1997
Flückiger 2006
-
- Flückiger U, Marchetti O, Bille J, Eggimann P, Zimmerli S, Imhof A, et al. Treatment options of invasive fungal infections in adults. Swiss Medical Weekly 2006;136(29‐30):447‐63. - PubMed
Greene 2007
-
- Greene RE, Schlamm HT, Oestmann JW, Stark P, Durand C, Lortholary O, et al. Imaging findings in acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: clinical significance of the halo sign. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2007;44(3):373‐9. - PubMed
Guo 2015
-
- Guo J, Riebler A. meta 4diag : Bayesian bivariate meta‐analysis of diagnostic test studies for routine practice. Journal of Statistical Software 2015;83(1):1‐31.
Harbord 2007
-
- Harbord RM, Deeks JJ, Egger M, Whiting P, Sterne JAC. A unification of models for meta‐analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. Biostatistics 2007;8(2):239‐51. - PubMed
Hope 2005
-
- Hope WW, Walsh TJ, Denning DW. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2005;5(10):609‐22. - PubMed
Leeflang 2008
Lehmann 2008
-
- Lehmann LE, Hunfeld KP, Emrich T, Haberhausen G, Wissing H, Hoeft A, et al. A multiplex real‐time PCR assay for rapid detection and differentiation of 25 bacterial and fungal pathogens from whole blood samples. Medical Microbiology and Immunology 2008;197(3):313‐324. - PubMed
Lewis 2006
-
- Lewis PL, Barnes RA. Aspergillus PCR ‐ Platforms, strengths and weaknesses. Medical Mycology 2006;44((Supplement_1)):S191‐8. - PubMed
Lijmer 1999
-
- Lijmer JG, Mol BW, Heisterkamp S, Bonsel GJ, Prins MH, Meulen JH, et al. Empirical evidence of design‐related bias in studies of diagnostic tests. JAMA 1999;282(11):1061‐6. - PubMed
Loeffler 2000
Loeffler 2002
Marr 2002
-
- Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L. Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood 2002;100(13):4358‐66. - PubMed
Meersseman 2004
-
- Meersseman W, Vandecasteele SJ, Wilmer A, Verbeken E, Peetermans WE, Wijngaerden E. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients without malignancy. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2004;170(6):621‐5. - PubMed
Mengoli 2009
-
- Mengoli C, Cruciani M, Barnes RA, Loeffler J, Donnelly JP. Use of PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2009;9(2):89‐96. - PubMed
Pfeiffer 2006
-
- Pfeiffer CD, Fine JP, Safdar N. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis using a galactomannan assay: a meta‐analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006;42(10):1417‐27. - PubMed
Rath 2018
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(10):982‐90. - PubMed
Reitsma 2009
-
- Reitsma JB, Rutjes AWS, Whiting P, Vlassov VV, Leeflang MMG, Deeks JJ. Chapter 9: Assessing methodological quality. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from srdta.cochrane.org.
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Ribeiro 2006
-
- Ribeiro P, Costa F, Monteiro A, Caldas J, Silva M, Ferreira G, et al. Polymerase chain reaction screening for fungemia and/or invasive fungal infectionsin patients with hematologic malignancies. Supportive Care in Cancer 2006;14(5):469‐74. - PubMed
Rutter 2001
-
- Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta‐analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(19):2865‐84. - PubMed
Sachse 2009
-
- Sachse S, Straube E, Lehmann M, Bauer M, Russwurm S, Schmidt KH. Truncated human cytidylate‐phosphate‐deoxyguanylate‐binding protein for improved nucleic acid amplification technique‐based detection of bacterial species in human samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2009;47(4):1050‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Senn 2008
-
- Senn L, Robinson JO, Schmidt S, Knaup M, Asahi N, Satomura S, et al. 1,3‐Beta‐D‐glucan antigenemia for early diagnosis of invasive fungal infections in neutropenic patients with acute leukemia. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;46(6):878‐85. - PubMed
Shin 1999
Springer 2012
Tang 1993
-
- Tang CM, Holden DW, Aufauvre‐Brown A, Cohen J. The detection of Aspergillus spp. by the polymerase chain reaction and its evaluation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1993;148(5):1313‐7. - PubMed
Tuon 2007
-
- Tuon FF. A systematic literature review on the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from bronchoalveolar lavage clinical samples. Revista Iberoamericana de Micologia 2007;24(2):89‐94. - PubMed
Van Burik 1998
Walsh 2008
-
- Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, et al. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;46(3):327‐60. - PubMed
Watzinger 2004
White 2010
White 2015
Whiting 2004
-
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Dinnes J, Reitsma J, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies. Health Technology Assessment 2004;8:III(25):1‐234. - PubMed
Whiting 2005
Williamson 2000
-
- Williamson EC, Leeming JP, Palmer HM, Steward CG, Warnock D, Marks DI, et al. Diagnosis of invasiveaspergillosis in bone marrow transplant recipients by polymerase chain reaction. British Journal of Haematology 2000;108(1):132‐9. - PubMed
Yoo 2008
-
- Yoo JH, Choi SM, Choi JH, Kwon EY, Park C, Shin WS. Construction of internal control for the quantitative assay of Aspergillus fumigatus using real‐time nucleic acid sequence‐based amplification. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 2008;60(1):121‐4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

