Adaptation of hepatitis C virus to interferon lambda polymorphism across multiple viral genotypes
- PMID: 31478832
- PMCID: PMC6721370
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.42542
Adaptation of hepatitis C virus to interferon lambda polymorphism across multiple viral genotypes
Abstract
Genetic polymorphism in the interferon lambda (IFN-λ) region is associated with spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and response to interferon-based treatment. Here, we evaluate associations between IFN-λ polymorphism and HCV variation in 8729 patients (Europeans 77%, Asians 13%, Africans 8%) infected with various viral genotypes, predominantly 1a (41%), 1b (22%) and 3a (21%). We searched for associations between rs12979860 genotype and variants in the NS3, NS4A, NS5A and NS5B HCV proteins. We report multiple associations in all tested proteins, including in the interferon-sensitivity determining region of NS5A. We also assessed the combined impact of human and HCV variation on pretreatment viral load and report amino acids associated with both IFN-λ polymorphism and HCV load across multiple viral genotypes. By demonstrating that IFN-λ variation leaves a large footprint on the viral proteome, we provide evidence of pervasive viral adaptation to innate immune pressure during chronic HCV infection.
Keywords: Hepatitis C; genetics; genome to genome analysis; genomics; human; infectious disease; integration analysis; interferon lambda polymorphism; microbiology.
© 2019, Chaturvedi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NC, JF No competing interests declared, ES, HM, AO, DB, GS, JM This study was partially funded by Gilead Sciences and the author is an employee of Gilead Sciences, SZ has been a consultant for Abbvie, Gilead, Janssen, Merck/MSD
Figures
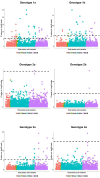
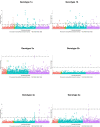
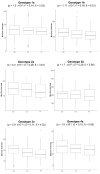
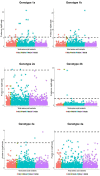
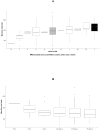
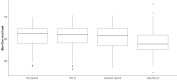
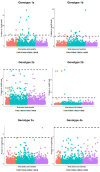
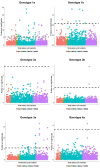
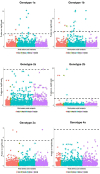
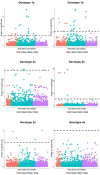
Comment in
-
What makes the hepatitis C virus evolve?Elife. 2019 Sep 3;8:e50148. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50148. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31478837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari MA, Pedergnana V, L C Ip C, Magri A, Von Delft A, Bonsall D, Chaturvedi N, Bartha I, Smith D, Nicholson G, McVean G, Trebes A, Piazza P, Fellay J, Cooke G, Foster GR, STOP-HCV Consortium. Hudson E, McLauchlan J, Simmonds P, Bowden R, Klenerman P, Barnes E, Spencer CCA. Genome-to-genome analysis highlights the effect of the human innate and adaptive immune systems on the hepatitis C virus. Nature Genetics. 2017;49:666–673. doi: 10.1038/ng.3835. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ansari AM. Evidence for a widespread effect of interferon lambda 4 on hepatitis C virus diversity. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences & Emerging Drugs. 2018 doi: 10.4172/2380-9477-C4-015. - DOI
-
- Bartha I, Carlson JM, Brumme CJ, McLaren PJ, Brumme ZL, John M, Haas DW, Martinez-Picado J, Dalmau J, López-Galíndez C, Casado C, Rauch A, Günthard HF, Bernasconi E, Vernazza P, Klimkait T, Yerly S, O'Brien SJ, Listgarten J, Pfeifer N, Lippert C, Fusi N, Kutalik Z, Allen TM, Müller V, Harrigan PR, Heckerman D, Telenti A, Fellay J. A genome-to-genome analysis of associations between human genetic variation, HIV-1 sequence diversity, and viral control. eLife. 2013;2:e01123. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

