A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based computer programs to analyze chest x-rays for pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 31479448
- PMCID: PMC6719854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221339
A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based computer programs to analyze chest x-rays for pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
We undertook a systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based software for identification of radiologic abnormalities (computer-aided detection, or CAD) compatible with pulmonary tuberculosis on chest x-rays (CXRs). We searched four databases for articles published between January 2005-February 2019. We summarized data on CAD type, study design, and diagnostic accuracy. We assessed risk of bias with QUADAS-2. We included 53 of the 4712 articles reviewed: 40 focused on CAD design methods ("Development" studies) and 13 focused on evaluation of CAD ("Clinical" studies). Meta-analyses were not performed due to methodological differences. Development studies were more likely to use CXR databases with greater potential for bias as compared to Clinical studies. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (median AUC [IQR]) were significantly higher: in Development studies AUC: 0.88 [0.82-0.90]) versus Clinical studies (0.75 [0.66-0.87]; p-value 0.004); and with deep-learning (0.91 [0.88-0.99]) versus machine-learning (0.82 [0.75-0.89]; p = 0.001). We conclude that CAD programs are promising, but the majority of work thus far has been on development rather than clinical evaluation. We provide concrete suggestions on what study design elements should be improved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
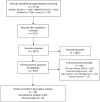



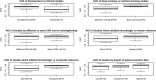
References
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2017. Geneva: Licence: CC BY-NC- SA 3.0 IGO.: World Health Organization, 2017.
-
- WILLIAMS FH. The Use of X-Ray Examinations in Pulmonary Tuberculosis. The Boston Medical and Surgical Journal. 1907;157(26):850–3. 10.1056/nejm190712261572602 - DOI
-
- Chunhaswasdikul B, Kamolratanakul P, Jittinandana A, Tangcharoensathien V, Kuptawintu S, Pantumabamrung P. Anti-tuberculosis programs in Thailand: a cost analysis. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1992;23(2):195–9. Epub 1992/06/01. . - PubMed
-
- WHO. Chest Radiography in Tuberculosis Detection—Summary of current WHO recommendations and guidance on programmatic approaches. 2016 2016. Report No.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

