Exercise Reduces Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Mediating the lncRNA MALAT1/MicroRNA-382-3p/Resistin Axis
- PMID: 31479923
- PMCID: PMC6726922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.08.002
Exercise Reduces Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Mediating the lncRNA MALAT1/MicroRNA-382-3p/Resistin Axis
Abstract
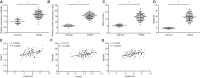
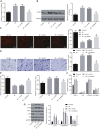
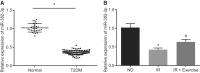
Insulin resistance (IR) is the primary pathological mechanism underlying type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Here, the study aimed to ascertain whether and how exercise mediates IR in T2DM. An in vivo mouse model of high-fat diet-induced IR and an in vitro high-glucose-induced IR model were constructed. High long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) expression was detected in T2MD and was positively correlated with HOMA-IR and resistin levels. Then, short hairpin RNA targeting MALAT1 (sh-MALAT1) or pcDNA-MALAT1 was delivered into human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to knock down or upregulate its expression, respectively. Silencing of MALAT1 resulted in reduced levels of resistin, Ang II, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and p-insulin receptor substrate-1 (p-IRS)/ISR-1, and decreased cell migration, as well as enhanced glucose uptake and levels of nitric oxide (NO) and p-Akt/Akt. In the IR mouse model, exercise was observed to downregulate MALAT1 to reduce resistin, whereby exercise reduced homeostatic model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Besides, exercise also elevated microRNA-382-3p (miR-382-3p) expression in the serum of IR mice. Dual-luciferase reporter and RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays identified that MALAT1 could bind to miR-382-3p to upregulate resistin. Collectively, the key observations of the study provide evidence that inhibition of MALAT1 elevates miR-382-3p to repress resistin, which consequently underlies the mechanism of exercise protecting against IR, highlighting a direction for T2DM therapy development.
Keywords: exercise; insulin resistance; metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; microRNA-382-3p; resistin; type 2 diabetes mellitus; vascular endothelial cells.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Demethylation of miR-299-5p by aerobic exercise relieves insulin resistance in the vascular endothelium by repressing resistin.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023 Jan;195:110176. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110176. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 36427628
-
Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells by regulating miR-361-3p/SOCS3 axis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 May 1;13(5):1243-1252. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32509100 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic exercise improves cognitive impairment in mice with type 2 diabetes by regulating the MALAT1/miR-382-3p/BDNF signaling pathway in serum-exosomes.Mol Med. 2023 Sep 22;29(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00727-1. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37740187 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting lncRNA MALAT1: A Promising Approach to Overcome Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Endocrinol. 2024 Oct 28;2024:1821252. doi: 10.1155/2024/1821252. eCollection 2024. Int J Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39502508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and mechanisms of lncRNA MALAT1 in cancer chemotherapy resistance.Biomark Res. 2023 Feb 24;11(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00467-8. Biomark Res. 2023. PMID: 36829256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pervasive Small RNAs in Cardiometabolic Research: Great Potential Accompanied by Biological and Technical Barriers.Diabetes. 2020 May;69(5):813-822. doi: 10.2337/dbi19-0015. Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32312897 Free PMC article.
-
The epigenetic landscape of exercise in cardiac health and disease.J Sport Health Sci. 2021 Dec;10(6):648-659. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2020.12.003. Epub 2020 Dec 14. J Sport Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 33333247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Potential Function as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets of Exercise Training.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Jan 9. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10586-8. Online ahead of print. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39786669 Review.
-
The Impact of lncRNAs in Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and In Silico Analyses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 19;12:602597. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.602597. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33815273 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Ameliorates Insulin Resistance of Type 2 Diabetes through Motivating Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Mediated Skeletal Muscle Cell Autophagy.Biology (Basel). 2020 Aug 3;9(8):203. doi: 10.3390/biology9080203. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32756447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corona G., Monami M., Rastrelli G., Aversa A., Sforza A., Lenzi A., Forti G., Mannucci E., Maggi M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and testosterone: a meta-analysis study. Int. J. Androl. 2011;34:528–540. - PubMed
-
- Johnson A.M., Olefsky J.M. The origins and drivers of insulin resistance. Cell. 2013;152:673–684. - PubMed
-
- Szendroedi J., Phielix E., Roden M. The role of mitochondria in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011;8:92–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

