Cafestol and Kahweol: A Review on Their Bioactivities and Pharmacological Properties
- PMID: 31480213
- PMCID: PMC6747192
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20174238
Cafestol and Kahweol: A Review on Their Bioactivities and Pharmacological Properties
Abstract
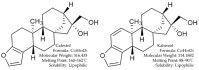
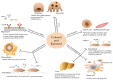
Cafestol and kahweol are natural diterpenes extracted from coffee beans. In addition to the effect of raising serum lipid, in vitro and in vivo experimental results have revealed that the two diterpenes demonstrate multiple potential pharmacological actions such as anti-inflammation, hepatoprotective, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, and anti-osteoclastogenesis activities. The most relevant mechanisms involved are down-regulating inflammation mediators, increasing glutathione (GSH), inducing apoptosis of tumor cells and anti-angiogenesis. Cafestol and kahweol show similar biological activities but not exactly the same, which might due to the presence of one conjugated double bond on the furan ring of the latter. This review aims to summarize the pharmacological properties and the underlying mechanisms of cafestol-type diterpenoids, which show their potential as functional food and multi-target alternative medicine.
Keywords: anti-diabetes; anti-inflammation; anti-tumor; cafestol; kahweol; serum lipid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
-
- Ding M., Bhupathiraju S.N., Satija A., van Dam R.M., Hu F.B. Long-term coffee consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Circulation. 2014;129:643–659. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

