Characterizing micro-to-millisecond chemical exchange in nucleic acids using off-resonance R1ρ relaxation dispersion
- PMID: 31481159
- PMCID: PMC6727989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2019.05.002
Characterizing micro-to-millisecond chemical exchange in nucleic acids using off-resonance R1ρ relaxation dispersion
Abstract
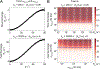
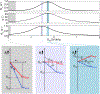
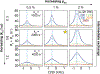
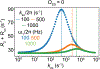
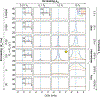
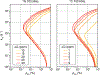
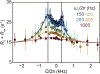
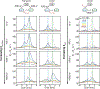
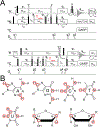
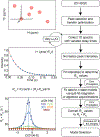
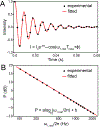
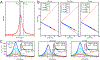
This review describes off-resonance R1ρ relaxation dispersion NMR methods for characterizing microsecond-to-millisecond chemical exchange in uniformly 13C/15N labeled nucleic acids in solution. The review opens with a historical account of key developments that formed the basis for modern R1ρ techniques used to study chemical exchange in biomolecules. A vector model is then used to describe the R1ρ relaxation dispersion experiment, and how the exchange contribution to relaxation varies with the amplitude and frequency offset of an applied spin-locking field, as well as the population, exchange rate, and differences in chemical shifts of two exchanging species. Mathematical treatment of chemical exchange based on the Bloch-McConnell equations is then presented and used to examine relaxation dispersion profiles for more complex exchange scenarios including three-state exchange. Pulse sequences that employ selective Hartmann-Hahn cross-polarization transfers to excite individual 13C or 15N spins are then described for measuring off-resonance R1ρ(13C) and R1ρ(15N) in uniformly 13C/15N labeled DNA and RNA samples prepared using commercially available 13C/15N labeled nucleotide triphosphates. Approaches for analyzing R1ρ data measured at a single static magnetic field to extract a full set of exchange parameters are then presented that rely on numerical integration of the Bloch-McConnell equations or the use of algebraic expressions. Methods for determining structures of nucleic acid excited states are then reviewed that rely on mutations and chemical modifications to bias conformational equilibria, as well as structure-based approaches to calculate chemical shifts. Applications of the methodology to the study of DNA and RNA conformational dynamics are reviewed and the biological significance of the exchange processes is briefly discussed.
Keywords: Chemical exchange; Hoogsteen; Nucleic acid dynamics; R(1ρ) relaxation dispersion; Tautomers.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
Hashim M. Al-Hashimi (H.M.A.) is an advisor to and holds an ownership interest in Nymirum Inc., which is an RNA-based drug discovery company. The research reported in this article was performed by Duke University faculty and students and was funded by NIH and NIGMS contracts to H.M.A.
Figures

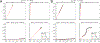
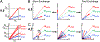

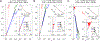
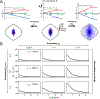

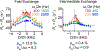
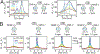
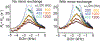
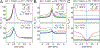

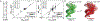
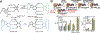
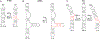
References
-
- Watson JD, Crick FHC, A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid, Nature, 171 (1953) 737–738. - PubMed
-
- Bardaro MF Jr., Varani G, Examining the relationship between RNA function and motion using nuclear magnetic resonance, Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. RNA, 3 (2012) 122–132. - PubMed
-
- Rinnenthal J, Buck J, Ferner J, Wacker A, Furtig B, Schwalbe H, Mapping the landscape of RNA dynamics with NMR spectroscopy, Accounts of chemical research, 44 (2011) 1292–1301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

