Growth Phase-Dependent Chromosome Condensation and Heat-Stable Nucleoid-Structuring Protein Redistribution in Escherichia coli under Osmotic Stress
- PMID: 31481544
- PMCID: PMC6832063
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00469-19
Growth Phase-Dependent Chromosome Condensation and Heat-Stable Nucleoid-Structuring Protein Redistribution in Escherichia coli under Osmotic Stress
Abstract
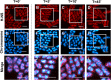
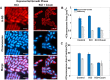
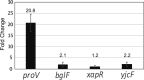
The heat-stable nucleoid-structuring (H-NS) protein is a global transcriptional regulator implicated in coordinating the expression of over 200 genes in Escherichia coli, including many involved in adaptation to osmotic stress. We have applied superresolved microscopy to quantify the intracellular and spatial reorganization of H-NS in response to a rapid osmotic shift. We found that H-NS showed growth phase-dependent relocalization in response to hyperosmotic shock. In stationary phase, H-NS detached from a tightly compacted bacterial chromosome and was excluded from the nucleoid volume over an extended period of time. This behavior was absent during rapid growth but was induced by exposing the osmotically stressed culture to a DNA gyrase inhibitor, coumermycin. This chromosomal compaction/H-NS exclusion phenomenon occurred in the presence of either potassium or sodium ions and was independent of the presence of stress-responsive sigma factor σS and of the H-NS paralog StpA.IMPORTANCE The heat-stable nucleoid-structuring (H-NS) protein coordinates the expression of over 200 genes in E. coli, with a large number involved in both bacterial virulence and drug resistance. We report on the novel observation of a dynamic compaction of the bacterial chromosome in response to exposure to high levels of salt. This stress response results in the detachment of H-NS proteins and their subsequent expulsion to the periphery of the cells. We found that this behavior is related to mechanical properties of the bacterial chromosome, in particular, to how tightly twisted and coiled is the chromosomal DNA. This behavior might act as a biomechanical response to stress that coordinates the expression of genes involved in adapting bacteria to a salty environment.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; H-NS; chromosome organization; nucleoid-associated proteins; osmotic stress; stress response.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Hommais F, Krin E, Laurent-Winter C, Soutourina O, Malpertuy A, Le Caer J-P, Danchin A, Bertin P. 2001. Large-scale monitoring of pleiotropic regulation of gene expression by the prokaryotic nucleoid-associated protein, H-NS. Mol Microbiol 40:20–36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02358.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

