Extracellular RNA in a single droplet of human serum reflects physiologic and disease states
- PMID: 31481608
- PMCID: PMC6754586
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1908252116
Extracellular RNA in a single droplet of human serum reflects physiologic and disease states
Abstract
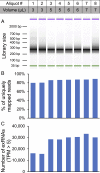
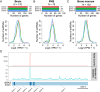
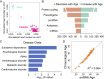
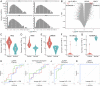
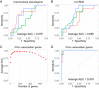
Extracellular RNAs (exRNAs) are present in human serum. It remains unclear to what extent these circulating exRNAs may reflect human physiologic and disease states. Here, we developed SILVER-seq (Small Input Liquid Volume Extracellular RNA Sequencing) to efficiently sequence both integral and fragmented exRNAs from a small droplet (5 μL to 7 μL) of liquid biopsy. We calibrated SILVER-seq in reference to other RNA sequencing methods based on milliliters of input serum and quantified droplet-to-droplet and donor-to-donor variations. We carried out SILVER-seq on more than 150 serum droplets from male and female donors ranging from 18 y to 48 y of age. SILVER-seq detected exRNAs from more than a quarter of the human genes, including small RNAs and fragments of mRNAs and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). The detected exRNAs included those derived from genes with tissue (e.g., brain)-specific expression. The exRNA expression levels separated the male and female samples and were correlated with chronological age. Noncancer and breast cancer donors exhibited pronounced differences, whereas donors with or without cancer recurrence exhibited moderate differences in exRNA expression patterns. Even without using differentially expressed exRNAs as features, nearly all cancer and noncancer samples and a large portion of the recurrence and nonrecurrence samples could be correctly classified by exRNA expression values. These data suggest the potential of using exRNAs in a single droplet of serum for liquid biopsy-based diagnostics.
Keywords: age; biomarker; breast cancer; cancer recurrence; extracellular RNA.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A provisional patent is filed. S.Z. is a cofounder of Genemo, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply to Hartl and Gao: Lack of between-batch difference in the distributions of measured extracellular RNA levels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 28;117(4):1851-1852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918079117. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31964851 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clarifying the effect of library batch on extracellular RNA sequencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 28;117(4):1849-1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916312117. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31964852 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
When DNA gets in the way: A cautionary note for DNA contamination in extracellular RNA-seq studies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 11;117(32):18934-18936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001675117. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32788394 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Verwilt et al.: Experimental evidence against DNA contamination in SILVER-seq.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 11;117(32):18937-18938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008585117. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32788395 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Human plasma and serum extracellular small RNA reference profiles and their clinical utility.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jun 5;115(23):E5334-E5343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714397115. Epub 2018 May 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29777089 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-RNA-seq: a modified small RNA-seq method that reveals circulating mRNA and lncRNA fragments as potential biomarkers in human plasma.EMBO J. 2019 Jun 3;38(11):e101695. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101695. Epub 2019 May 3. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31053596 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of long extracellular RNAs reveals a detection panel of noncoding RNAs for liver cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(1):181-193. doi: 10.7150/thno.48206. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391469 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating RNAs in prostate cancer patients.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jan 1;524:57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.011. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 34656688 Review.
-
Liquid Biopsy beyond Circulating Tumor Cells and Cell-Free DNA.Acta Cytol. 2019;63(6):479-488. doi: 10.1159/000493969. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Acta Cytol. 2019. PMID: 30783027 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of RNU44 as an Endogenous Reference Gene for Normalizing Cell-Free RNA in Tuberculosis.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 9;9(12):ofac540. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac540. eCollection 2022 Dec. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36519116 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free RNA as a Novel Biomarker for Response to Therapy in Head & Neck Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 May 6;12:869108. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.869108. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35600369 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus serum RNA transcript isoform composition and proportion in chronic hepatitis B patients by nanopore long-read sequencing.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 14;14:1233178. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1233178. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37645229 Free PMC article.
-
Clarifying the effect of library batch on extracellular RNA sequencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 28;117(4):1849-1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916312117. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31964852 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Extracellular tRNAs and tRNA-derived fragments.RNA Biol. 2020 Aug;17(8):1149-1167. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1729584. Epub 2020 Feb 19. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 32070197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heitzer E., Haque I. S., Roberts C. E. S., Speicher M. R., Current and future perspectives of liquid biopsies in genomics-driven oncology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 20, 71–88 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Alimirzaie S., Bagherzadeh M., Akbari M. R., Liquid biopsy in breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Clin. Genet. 95, 643–660 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

