Discovery of Ethyl 2-Nitro-3-Arylacrylates Molecules as T3SS Inhibitor Reducing the Virulence of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria Xanthomonas
- PMID: 31481941
- PMCID: PMC6710329
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01874
Discovery of Ethyl 2-Nitro-3-Arylacrylates Molecules as T3SS Inhibitor Reducing the Virulence of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria Xanthomonas
Abstract
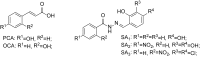
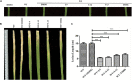
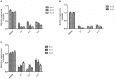
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is a gram-negative pathogen which causes leaf blight disease. Known traditional bactericides are not much more effective in inhibiting this bacteria than before. Selecting the virulence factor of the bacteria as the target without affecting their growth has been considered as a novel method for developing new anti-microbial drugs. Type III secretion systems (T3SS) are one of the important and highly conserved virulence factors in most gram-negative pathogens, which has been considered as an effective target to develop new anti-microbial drugs. In order to discover potential anti-microbial drugs against Xoo pathogens, a series of ethyl 2-nitro-3-arylacrylates compounds were screened. Among them, the compounds I-9, I-12, and I-13 could highly inhibit the promoter activity of a harpin gene hpa1, which were used to further check for the influence on bacterial growth and on the hypersensitive response (HR) caused by Xoo bacteria on non-host plants. The results showed that above compounds could reduce HR without affecting bacterial growth and survival. Moreover, qRT-PCR analysis indicated that treatment with the three inhibitors (I-9, I-12, and I-13) could suppress the expression of the Xoo T3SS in different extent. The mRNA levels of representative genes in the hrp cluster, including the key regulatory genes hrpG and hrpX, were decreased. Last but not least, in vivo test ensured that the above compounds reduced the disease symptoms of Xoo on the rice and Xcc on the Chinese radish.
Keywords: Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc); Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo); anti-virulence compounds; ethyl 2-nitro-3-arylacrylates molecules; type III secretion system (T3SS).
Figures



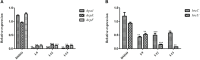




Similar articles
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Targeting the Type III Secretion System of Xanthomonas oryzae on Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 23;20(4):971. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040971. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30813400 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and bioactivity of thiazolidin-2-cyanamide derivatives against type III secretion system of Xanthomonas oryzae on rice.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018 Jul;149:89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30033022
-
Identification of phenolic compounds that suppress the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae on rice via the type III secretion system.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 May;18(4):555-568. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12415. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27084974 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review.Rice (N Y). 2020 Jan 8;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 31915945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HrpG/HrpX Regulon of Xanthomonads-An Insight to the Complexity of Regulation of Virulence Traits in Phytopathogenic Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2021 Jan 16;9(1):187. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010187. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33467109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on Small Molecular Inhibitors of the Type 3 Secretion System.Molecules. 2022 Nov 30;27(23):8348. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238348. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five Plant Natural Products Are Potential Type III Secretion System Inhibitors to Effectively Control Soft-Rot Disease Caused by Dickeya.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 22;13:839025. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.839025. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35273588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowlin N. O., Williams J. D., Knoten C. A., Torhan M. C., Tashjian T. F., Li B., et al. (2014). Mutations in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa needle protein gene pscF confer resistance to phenoxyacetamide inhibitors of the type III secretion system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 2211–2220. 10.1128/AAC.02795-13 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

