The Fibrosis and Immunological Features of Hypochlorous Acid Induced Mouse Model of Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 31481954
- PMCID: PMC6710365
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01861
The Fibrosis and Immunological Features of Hypochlorous Acid Induced Mouse Model of Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
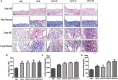
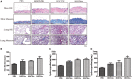
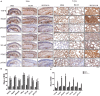
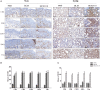
Fibrotic animal models are critical for the pathogenesis investigations and drug explorations in systemic sclerosis (SSc). The bleomycin (BLM)-induced mouse model is the classical and most widely used fibrosis model. However, traditional subcutaneous injection of BLM rarely induced diffuse skin and lung lesions. Hypochlorous acid (HOCl)-induced mice are a more representative model that have diffuse cutaneous lesions, lung fibrosis and renal involvement. However, the fibrotic and immunological features of this model are not fully elucidated. Here, we injected BALB/c mice subcutaneously with HOCl used at different concentrations of HOCl (1:55, 1:70, and 1:110 NaClO: KH2PO4, hereafter named HOCl55, HOCl70, and HOCl110, respectively) for 6 weeks to induce fibrosis, and also used HOCl110 at different time course (4, 5, and 6 weeks). Morphological changes were observed via HE and Masson's trichrome staining. Immunohistochemistry or real-time PCR was used to detect inflammatory infiltrates, important fibrosis pathways and pro-inflammatory mediator expression. Flow cytometry was used to detect the alteration of immune cells in mouse spleen. Skin and lung fibrosis were most obvious in the HOCl55 group compared to lower concentration groups. In the HOCl110 group, dominant inflammatory infiltrates were found after 5 weeks, and significant fibrosis was found after 6 weeks. Then we explored the fibrosis and immunological profiles in the HOCl110 (6 weeks) group. Important fibrosis pathway proteins such as TGF-β, NF-κB, Smad3, p-Smad3, STAT3, and p-STAT3 were significantly elevated at week 6 in the HOCl110 group. Increased infiltration of CD4+T cells, CD8+T cells, CD20+B cells, and myofibroblasts was found both in skin and lung tissues. However, decreased CD4+T cells, CD8+T cells, monocytes and macrophages and increased CD19+B cells were found in the spleen tissues. The mRNA expression of fibrosis mediators such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, IL-33, TNF-α, and CTGF was also upregulated in skin and lung tissues. In conclusion, HOCl induced fibrosis mouse model displayed systemic immune cell infiltration, pro-inflammatory mediator release, vasculopathy and fibrosis, which better mimicked human SSc than BLM-induced mice.
Keywords: HOCl-induced mice; SSc; fibrosis; immune cell infiltration; pro-inflammatory mediators.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated frequencies of CD4(+) IL-21(+) T, CD4(+) IL-21R(+) T and IL-21(+) Th17 cells, and increased levels of IL-21 in bleomycin-induced mice may be associated with dermal and pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Apr;19(4):392-404. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12522. Epub 2014 Dec 25. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25545680
-
Th17 cells and IL-17 promote the skin and lung inflammation and fibrosis process in a bleomycin-induced murine model of systemic sclerosis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;34 Suppl 100(5):14-22. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26750756
-
Effects of thalidomide on Th17, Treg cells and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway in a mouse model of systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Mar;23(3):406-419. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13769. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31840939
-
New insights on chemically induced animal models of systemic sclerosis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Nov;23(6):511-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32834b1606. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21857225 Review.
-
Skin and lung fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice: a systematic review.Reumatismo. 2024 Mar 22;76(1). doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2024.1642. Reumatismo. 2024. PMID: 38523580
Cited by
-
Lactococcus garvieae exerts a critical role in inducing inflammation in dairy mastitis by triggering NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in MAC-T cells.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 12;40(4):132. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-03947-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38470533
-
The Potential of Twendee X® as a Safe Antioxidant Treatment for Systemic Sclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 6;25(5):3064. doi: 10.3390/ijms25053064. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474309 Free PMC article.
-
IFIT3 mediates TBK1 phosphorylation to promote activation of pDCs and exacerbate systemic sclerosis in mice.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Sep;14(9):e1800. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1800. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39305055 Free PMC article.
-
Simple gene signature to assess murine fibroblast polarization.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 11;12(1):11748. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15640-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35817787 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models of Systemic Sclerosis: Using Nailfold Capillaroscopy as a Potential Tool to Evaluate Microcirculation and Microangiopathy: A Narrative Review.Life (Basel). 2022 May 8;12(5):703. doi: 10.3390/life12050703. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

