The Prognostic Significance of Protein Expression of CASZ1 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 31481981
- PMCID: PMC6701416
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1342161
The Prognostic Significance of Protein Expression of CASZ1 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Backgrounds: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common histologic subtype of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and shows a relatively poor prognosis among RCCs. Castor zinc finger 1 (CASZ1) is a transcription factor, prominently known for its tumor suppression role in neuroblastoma and other cancers. However, there has been no research about the prognostic significance of CASZ1 in ccRCC. In this study, we investigated CASZ1 expression in ccRCC and analyzed its prognostic implications.
Methods: A total of 896 ccRCC patients, who underwent surgical resection from 1995 to 2008, were included. We prepared tissue microarray blocks, evaluated CASZ1 nuclear expression by immunohistochemistry, and classified the cases into low or high expression categories.
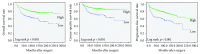
Results: A low expression of CASZ1 was observed in 320 cases (35.7%) and was significantly associated with large tumor size, high World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology (WHO/ISUP) grade, and high T category and M category. In survival analysis, a low expression of CASZ1 was significantly correlated with unfavorable progression-free survival (PFS) (p < 0.001), overall survival (OS) (p < 0.001), and cancer-specific survival (CSS) (p < 0.001) and was an independent prognostic factor for PFS and CSS in multivariate analysis adjusted for tumor size, WHO/ISUP grade, T category, N category, and M category.
Conclusions: Our study is the first to show the prognostic significance of CASZ1 expression in ccRCC. Our results revealed that low expression of CASZ1 is associated with poor prognosis and may serve as a new prognostic indicator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical