MicroRNA-29a inhibits glioblastoma stem cells and tumor growth by regulating the PDGF pathway
- PMID: 31482267
- PMCID: PMC10880555
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-019-03275-z
MicroRNA-29a inhibits glioblastoma stem cells and tumor growth by regulating the PDGF pathway
Abstract
Background and purpose: microRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that play important roles in cancer regulation. In this study, we investigated the expression, functional effects and mechanisms of action of microRNA-29a (miR-29a) in glioblastoma (GBM).
Methods: miR-29a expression levels in GBM cells, stem cells (GSCs) and human tumors as well as normal astrocytes and normal brain were measured by quantitative PCR. miR-29a targets were uncovered by target prediction algorithms, and verified by immunoblotting and 3' UTR reporter assays. The effects of miR-29a on cell proliferation, death, migration and invasion were assessed with cell counting, Annexin V-PE/7AAD flow cytometry, scratch assay and transwell assay, respectively. Orthotopic xenografts were used to determine the effects of miR-29a on tumor growth.
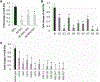
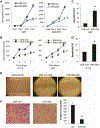
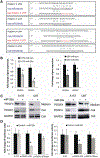
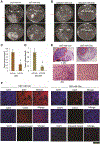
Results: Mir-29a was downregulated in human GBM specimens, GSCs and GBM cell lines. Exogenous expression of miR-29a inhibited GSC and GBM cell growth and induced apoptosis. miR-29a also inhibited GBM cell migration and invasion. PDGFC and PDGFA were uncovered and validated as direct targets of miR-29a in GBM. miR-29a downregulated PDGFC and PDGFA expressions at the transcriptional and translational levels. PDGFC and PDGFA expressions in GBM tumors, GSCs, and GBM established cell lines were higher than in normal brain and human astrocytes. Mir-29a expression inhibited orthotopic GBM xenograft growth.
Conclusions: miR-29a is a tumor suppressor miRNA in GBM, where it inhibits cancer stem cells and tumor growth by regulating the PDGF pathway.
Keywords: Glioblastoma (GBM); Glioblastoma stem cells (GSC); Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); microRNA (miRNA).
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

