Assessing Implementation Strategy Reporting in the Mental Health Literature: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 31482489
- PMCID: PMC6946851
- DOI: 10.1007/s10488-019-00965-8
Assessing Implementation Strategy Reporting in the Mental Health Literature: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Inadequate implementation strategy reporting restricts research synthesis and replicability. We explored the implementation strategy reporting quality of a sample of mental health articles using Proctor et al.'s (Implement Sci 8:139, 2013) reporting recommendations. We conducted a narrative review to generate the sample of articles and assigned a reporting quality score to each article. The mean article reporting score was 54% (range 17-100%). The most reported domains were: name (100%), action (82%), target (80%), and actor (67%). The least reported domains included definition (6%), temporality (26%), justification (34%), and outcome (37%). We discuss limitations and provide recommendations to improve reporting.
Keywords: Implementation strategies; Mental health; Reporting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
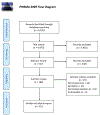
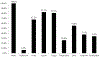
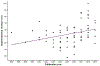
References
-
- Academy Health. (2017). 10th annual conference on the science of dissemination and implementation health: A decade of progress and the path forward Retrieved from https://www.academyhealth.org/events/site/10th-annual-conference-science....
-
- Albrecht L, Archibald M, Arseneau D, & Scott SD (2013). Development of a checklist to assess the quality of reporting of knowledge translation interventions using the Workgroup for Intervention Development and Evaluation Research (WIDER) recommendations. Implementation Science, 8, 52 10.1186/1748-5908-8-52 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altman DG, & Moher D (2014). Importance of transparent reporting of health research In Moher D, Altman DG, Schulz K, Simera I, Wager E (Eds). Guidelines for reporting health research: A user’s manual (pp.1–13). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell; 10.1002/9781118715598.ch1 - DOI
-
- Arksey H, & O'Malley L (2005). Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19–32. 10.1080/1364557032000119616 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

