Proteomics in gastroparesis: unique and overlapping protein signatures in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis
- PMID: 31482734
- PMCID: PMC6879892
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00115.2019
Proteomics in gastroparesis: unique and overlapping protein signatures in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis
Abstract
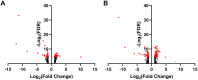
Macrophage-based immune dysregulation plays a critical role in development of delayed gastric emptying in diabetic mice. Loss of anti-inflammatory macrophages and increased expression of genes associated with pro-inflammatory macrophages has been reported in full-thickness gastric biopsies from gastroparesis patients. We aimed to determine broader protein expression (proteomics) and protein-based signaling pathways in gastric biopsies of diabetic (DG) and idiopathic gastroparesis (IG) patients. Additionally, we determined correlations between protein expressions, gastric emptying, and symptoms. Full-thickness gastric antrum biopsies were obtained from nine DG patients, seven IG patients, and five nondiabetic controls. Aptamer-based SomaLogic tissue scan that quantitatively identifies 1,305 human proteins was used. Protein fold changes were computed, and differential expressions were calculated using Limma. Ingenuity pathway analysis and correlations were carried out. Multiple-testing corrected P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Seventy-three proteins were differentially expressed in DG, 132 proteins were differentially expressed in IG, and 40 proteins were common to DG and IG. In both DG and IG, "Role of Macrophages, Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells" was the most statistically significant altered pathway [DG false discovery rate (FDR) = 7.9 × 10-9; IG FDR = 6.3 × 10-12]. In DG, properdin expression correlated with GCSI bloating (r = -0.99, FDR = 0.02) and expressions of prostaglandin G/H synthase 2, protein kinase C-ζ type, and complement C2 correlated with 4 h gastric retention (r = -0.97, FDR = 0.03 for all). No correlations were found between proteins and symptoms or gastric emptying in IG. Protein expression changes suggest a central role of macrophage-driven immune dysregulation in gastroparesis, specifically, complement activation in diabetic gastroparesis.NEW & NOTEWORTHY This study uses SOMAscan, a novel proteomics assay for determination of altered proteins and associated molecular pathways in human gastroparesis. Seventy-three proteins were changed in diabetic gastroparesis, 132 in idiopathic gastroparesis compared with controls. Forty proteins were common in both. Macrophage-based immune dysregulation pathway was most significantly affected in both diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. Proteins involved in the complement and prostaglandin synthesis pathway were associated with symptoms and gastric emptying delay in diabetic gastroparesis.
Keywords: diabetes; immune cells; inflammation; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures





References
-
- Bernard CE, Gibbons SJ, Mann IS, Froschauer L, Parkman HP, Harbison S, Abell TL, Snape WJ, Hasler WL, McCallum RW, Sarosiek I, Nguyen LA, Koch KL, Tonascia J, Hamilton FA, Kendrick ML, Shen KR, Pasricha PJ, Farrugia G; NIDDK Gastroparesis Clinical Research Consortium (GpCRC) . Association of low numbers of CD206-positive cells with loss of ICC in the gastric body of patients with diabetic gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 26: 1275–1284, 2014. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

