Female genital tract shedding of HIV-1 is rare in women with suppressed HIV-1 in plasma
- PMID: 31483374
- PMCID: PMC6910230
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002373
Female genital tract shedding of HIV-1 is rare in women with suppressed HIV-1 in plasma
Abstract
Objective: Determine the frequency of genital HIV-1 shedding in a large cohort of women on long-term suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART) and its association with mucosal inflammation.
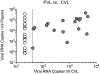
Design: We measured levels of HIV-1 RNA and inflammation biomarkers in cervicovaginal lavage (CVL) from HIV-seropositive women enrolled in the Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS).
Methods: HIV-1 was quantified (Abbott RealTime HIV-1 assay) from CVL samples of 332 WIHS participants with and without clinical evidence of genital inflammation at the time of CVL collection; participants had suppressed plasma viral load (PVL; limit of quantitation less than 20-4000 copies/ml depending on year of collection) for a median of 7.1 years [interquartile range (IQR) 3.4-9.8, Group 1] or for a median of 1.0 years (IQR = 0.5-1.0, Group 2). Twenty-two biomarkers of inflammation were measured in CVL to compare with clinical markers.
Results: HIV-1 was detected in 47% of 38 pre-ART CVL samples (median 668 copies/ml) and detection in CVL was associated with higher pre-ART PVL. HIV-1 was detected in only 1 of 38 CVL samples from these women on suppressive antiretroviral therapy for 1 year. No HIV-1 RNA was detected in 294 CVL samples from a cross-sectional set of women with suppressed PVL for a median of 7 years. Clinical inflammation markers were correlated with inflammatory biomarkers in CVL specimens, although genital inflammation was not associated with measurable genital HIV-1 shedding in these WIHS participants on ART.
Conclusion: ART that suppresses HIV-1 in the plasma of women also prevents genital tract HIV-1 shedding, even in the presence of genital tract inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Kovacs A, Wasserman SS, Burns D, Wright DJ, Cohn J, Landay A, et al. Determinants of HIV-1 shedding in the genital tract of women. Lancet 2001; 358:1593–1601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R38 AI140299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG062334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD001262/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG059505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

