Nonreciprocal and Conditional Cooperativity Directs the Pioneer Activity of Pluripotency Transcription Factors
- PMID: 31484078
- PMCID: PMC6750763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.103
Nonreciprocal and Conditional Cooperativity Directs the Pioneer Activity of Pluripotency Transcription Factors
Abstract
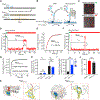
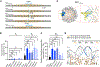
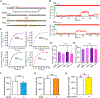
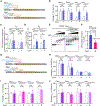
Cooperative binding of transcription factors (TFs) to chromatin orchestrates gene expression programming and cell fate specification. However, the biophysical principles of TF cooperativity remain incompletely understood. Here we use single-molecule fluorescence microscopy to study the partnership between Sox2 and Oct4, two core members of the pluripotency gene regulatory network. We find that the ability of Sox2 to target DNA inside nucleosomes is strongly affected by the translational and rotational positioning of its binding motif. In contrast, Oct4 can access nucleosomal sites with equal capacities. Furthermore, the Sox2-Oct4 pair displays nonreciprocal cooperativity, with Oct4 modulating interaction of Sox2 with the nucleosome but not vice versa. Such cooperativity is conditional upon the composite motif's residing at specific nucleosomal locations. These results reveal that pioneer factors possess distinct chromatin-binding properties and suggest that the same set of TFs can differentially regulate gene activities on the basis of their motif positions in the nucleosomal context.
Keywords: Oct4; Sox2; cooperative binding; gene regulatory network; nucleosome; pioneer activity; single-molecule fluorescence; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

