Ecdysone-Induced 3D Chromatin Reorganization Involves Active Enhancers Bound by Pipsqueak and Polycomb
- PMID: 31484080
- PMCID: PMC6754745
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.096
Ecdysone-Induced 3D Chromatin Reorganization Involves Active Enhancers Bound by Pipsqueak and Polycomb
Abstract
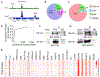
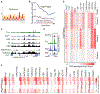
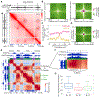
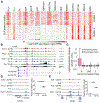
Evidence suggests that Polycomb (Pc) is present at chromatin loop anchors in Drosophila. Pc is recruited to DNA through interactions with the GAGA binding factors GAF and Pipsqueak (Psq). Using HiChIP in Drosophila cells, we find that the psq gene, which has diverse roles in development and tumorigenesis, encodes distinct isoforms with unanticipated roles in genome 3D architecture. The BR-C, ttk, and bab domain (BTB)-containing Psq isoform (PsqL) colocalizes genome-wide with known architectural proteins. Conversely, Psq lacking the BTB domain (PsqS) is consistently found at Pc loop anchors and at active enhancers, including those that respond to the hormone ecdysone. After stimulation by this hormone, chromatin 3D organization is altered to connect promoters and ecdysone-responsive enhancers bound by PsqS. Our findings link Psq variants lacking the BTB domain to Pc-bound active enhancers, thus shedding light into their molecular function in chromatin changes underlying the response to hormone stimulus.
Keywords: CTCF; GAF; HiChIP; POZ/BTB; Pipsqueak; architectural protein; chromatin; epigenetics; hormone; transcription.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The pipsqueak protein of Drosophila melanogaster binds to GAGA sequences through a novel DNA-binding domain.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):28504-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.28504. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9774480
-
Recruitment to Chromatin of (GA)n-Associated Factors GAF and Psq in the Transgenic Model System Depends on the Presence of Architectural Protein Binding Sites.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2022 Oct;506(1):210-214. doi: 10.1134/S1607672922050039. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 36303054
-
Control of germline torso expression by the BTB/POZ domain protein pipsqueak is required for embryonic terminal patterning in Drosophila.Genetics. 2011 Feb;187(2):513-21. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.121624. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21098720 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Architecture in the Fly: Living without CTCF/Cohesin Loop Extrusion?: Alternating Chromatin States Provide a Basis for Domain Architecture in Drosophila.Bioessays. 2019 Sep;41(9):e1900048. doi: 10.1002/bies.201900048. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 31264253 Review.
-
Chromatin insulators and long-distance interactions in Drosophila.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jan 3;588(1):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.10.039. Epub 2013 Nov 5. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24211836 Review.
Cited by
-
HiCrayon reveals distinct layers of multi-state 3D chromatin organization.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Dec 18;6(4):lqae182. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae182. eCollection 2024 Dec. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39703428 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila TET acts with PRC1 to activate gene expression independently of its catalytic activity.Sci Adv. 2024 May 3;10(18):eadn5861. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn5861. Epub 2024 May 3. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38701218 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative interactome analysis of the PRE DNA-binding factors: purification of the Combgap-, Zeste-, Psq-, and Adf1-associated proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 9;79(7):353. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04383-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35676368 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin alternates between A and B compartments at kilobase scale for subgenic organization.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 6;14(1):3303. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38429-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37280210 Free PMC article.
-
CLAMP and Zelda function together to promote Drosophila zygotic genome activation.Elife. 2021 Aug 3;10:e69937. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69937. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34342574 Free PMC article.

