The therapy of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: what is next?
- PMID: 31484664
- PMCID: PMC9488691
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0021-2019
The therapy of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: what is next?
Erratum in
-
"The therapy of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: what is next?" Vivien Somogyi, Nazia Chaudhuri, Sebastiano Emanuele Torrisi, et al. Eur Respir Rev 2019; 28: 190021.Eur Respir Rev. 2019 Sep 25;28(153):195021. doi: 10.1183/16000617.5021-2019. Print 2019 Sep 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2019. PMID: 31554706 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, fibrosing interstitial lung disease, characterised by progressive scarring of the lung and associated with a high burden of disease and early death. The pathophysiological understanding, clinical diagnostics and therapy of IPF have significantly evolved in recent years. While the recent introduction of the two antifibrotic drugs pirfenidone and nintedanib led to a significant reduction in lung function decline, there is still no cure for IPF; thus, new therapeutic approaches are needed. Currently, several clinical phase I-III trials are focusing on novel therapeutic targets. Furthermore, new approaches in nonpharmacological treatments in palliative care, pulmonary rehabilitation, lung transplantation, management of comorbidities and acute exacerbations aim to improve symptom control and quality of life. Here we summarise new therapeutic attempts and potential future approaches to treat this devastating disease.
Copyright ©ERS 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: V. Somogyi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Chaudhuri has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S.E. Torrisi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Kahn has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: V. Müller has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Kreuter has nothing to disclose.
Figures
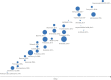
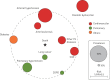
References
-
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018; 198: e44–e68. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: lessons from clinical trials over the past 25 years. Eur Respir J 2017; 50: 1701209. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Johnson WC, Lockhart D, et al. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with a new antifibrotic agent, pirfenidone: results of a prospective, open-label phase II study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 159: 1061–1069. - PubMed
-
- Azuma A, Nukiwa T, Tsuboi E, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171: 1040–1047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
