Genome-wide identification of Pseudomonas syringae genes required for fitness during colonization of the leaf surface and apoplast
- PMID: 31484768
- PMCID: PMC6754560
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1908858116
Genome-wide identification of Pseudomonas syringae genes required for fitness during colonization of the leaf surface and apoplast
Abstract
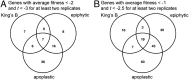
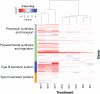
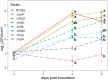
The foliar plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae can establish large epiphytic populations on leaf surfaces before apoplastic colonization. However, the bacterial genes that contribute to these lifestyles have not been completely defined. The fitness contributions of 4,296 genes in P. syringae pv. syringae B728a were determined by genome-wide fitness profiling with a randomly barcoded transposon mutant library that was grown on the leaf surface and in the apoplast of the susceptible plant Phaseolus vulgaris Genes within the functional categories of amino acid and polysaccharide (including alginate) biosynthesis contributed most to fitness both on the leaf surface (epiphytic) and in the leaf interior (apoplast), while genes involved in type III secretion system and syringomycin synthesis were primarily important in the apoplast. Numerous other genes that had not been previously associated with in planta growth were also required for maximum epiphytic or apoplastic fitness. Fourteen hypothetical proteins and uncategorized glycosyltransferases were also required for maximum competitive fitness in and on leaves. For most genes, no relationship was seen between fitness in planta and either the magnitude of their expression in planta or degree of induction in planta compared to in vitro conditions measured in other studies. A lack of association of gene expression and fitness has important implications for the interpretation of transcriptional information and our broad understanding of plant-microbe interactions.
Keywords: endophytes; epiphytes; gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lindemann J., Arny D. C., Upper C. D., Use of an apparent infection threshold population of Pseudomonas syringae to predict incidence and severity of brown spot of bean. Phytopathology 74, 1334–1339 (1984).
-
- Hirano S. S., Upper C. D., Ecology and epidemiology of foliar bacterial plant pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 21, 243–269 (1983).
-
- van der Wal A., Leveau J. H. J., Modelling sugar diffusion across plant leaf cuticles: The effect of free water on substrate availability to phyllosphere bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 792–797 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

