Overcoming adaptive therapy resistance in AML by targeting immune response pathways
- PMID: 31484791
- PMCID: PMC6985905
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw8828
Overcoming adaptive therapy resistance in AML by targeting immune response pathways
Abstract
Targeted inhibitors to oncogenic kinases demonstrate encouraging clinical responses early in the treatment course; however, most patients will relapse because of target-dependent mechanisms that mitigate enzyme-inhibitor binding or through target-independent mechanisms, such as alternate activation of survival and proliferation pathways, known as adaptive resistance. Here, we describe mechanisms of adaptive resistance in FMS-like receptor tyrosine kinase (FLT3)-mutant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by examining integrative in-cell kinase and gene regulatory network responses after oncogenic signaling blockade by FLT3 inhibitors (FLT3i). We identified activation of innate immune stress response pathways after treatment of FLT3-mutant AML cells with FLT3i and showed that innate immune pathway activation via the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 and 4 (IRAK1/4) complex contributes to adaptive resistance in FLT3-mutant AML cells. To overcome this adaptive resistance mechanism, we developed a small molecule that simultaneously inhibits FLT3 and IRAK1/4 kinases. The multikinase FLT3-IRAK1/4 inhibitor eliminated adaptively resistant FLT3-mutant AML cells in vitro and in vivo and displayed superior efficacy as compared to current targeted FLT3 therapies. These findings uncover a polypharmacologic strategy for overcoming adaptive resistance to therapy in AML by targeting immune stress response pathways.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
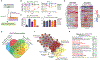

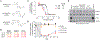


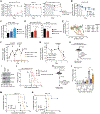
Comment in
-
FLT3-IRAK dual targeting: an exciting new therapeutic option guided by adaptive activation of immune response pathways.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Apr;8(7):511. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.21. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32395555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Griffith J, Black J, Faerman C, Swenson L, Wynn M, Lu F, Lippke J, Saxena K, The structural basis for autoinhibition of FLT3 by the juxtamembrane domain. Mol. Cell 13, 169–178 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Gilliland DG, Griffin JD, The roles of FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood 100, 1532–1542 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

