Combination treatment with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and ursodeoxycholic acid dissolves cholesterol gallstones in mice
- PMID: 31484954
- PMCID: PMC6726655
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49095-z
Combination treatment with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and ursodeoxycholic acid dissolves cholesterol gallstones in mice
Abstract
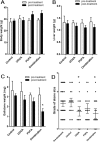
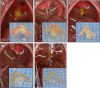
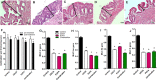
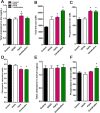
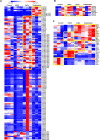
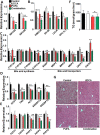
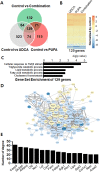
The increasing prevalence of cholesterol gallstone disease places an economic burden on the healthcare system. To identify novel therapeutics, we assessed the effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in combination with UDCA in a mouse model of cholesterol gallstones. Gallstone dissolution, gallbladder wall thickness, mucin gene expression in the gallbladder, and levels of phospholipids, cholesterol, and bile acids in bile and serum were analysed. RNA was extracted from the liver for mRNA sequencing and gene expression profiling. Combination treatment resulted in greater gallstone dissolution compared with the control group, and PUFA and combination treatments reduced the thickness of the gallbladder wall. Expression levels of mucin genes were significantly lower in the UDCA, PUFA, and combination groups. Transcriptome analyses revealed that combination treatment modulated hepatic lipid metabolism. The PUFA and combination groups showed elevated bile phospholipid and bile acid levels and a lower cholesterol saturation index. Combination treatment with PUFA and UDCA dissolves cholesterol gallstones in mice by decreasing mucin production, increasing levels of phospholipids and bile acids in bile, and decreasing cholesterol saturation. Further studies of the therapeutic effects of combination PUFA and UDCA treatment in patients with cholesterol gallstones are warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid attenuates cholesterol gallstones by suppressing mucin production with a high cholesterol diet in mice.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Nov;27(11):1745-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07227.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22849613
-
Gallstone Dissolution Effects of Combination Therapy with n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Ursodeoxycholic Acid: A Randomized, Prospective, Preliminary Clinical Trial.Gut Liver. 2024 Nov 15;18(6):1069-1079. doi: 10.5009/gnl230494. Epub 2024 May 7. Gut Liver. 2024. PMID: 38712398 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on the relative expression of the lipid metabolism genes in mouse cholesterol gallstone models.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jul 2;19(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01334-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32615989 Free PMC article.
-
Gallbladder bile supersaturated with cholesterol in gallstone patients preferentially develops from shortage of bile acids.J Lipid Res. 2019 Mar;60(3):498-505. doi: 10.1194/jlr.S091199. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30610083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Innovations in the medical treatment of gallstones and fatty liver: FABACs (Fatty Acid Bile Acid Conjugates)].Harefuah. 2008 Apr;147(4):344-9, 373, 372. Harefuah. 2008. PMID: 18686819 Review. Hebrew.
Cited by
-
Non-Surgical Management of Gallstones During Pregnancy: A Clinical Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Dec 29;16(12):e76560. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76560. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39881907 Free PMC article.
-
Association of dietary quality indicators with gallstones in the US: NHANES 2017-2020.BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 12;25(1):976. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21783-8. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40075394 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic profiles of incident gallstone disease.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 28;11(1):e001417. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2024-001417. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39209332 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental and Lifestyle Risk Factors in the Carcinogenesis of Gallbladder Cancer.J Pers Med. 2022 Feb 8;12(2):234. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020234. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid: A Pharmaco-Nutraceutical Approach to Improve the Responsiveness to Ursodeoxycholic Acid.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 29;13(8):2617. doi: 10.3390/nu13082617. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaheen Nicholas J, Hansen Richard A, Morgan Douglas R, Gangarosa Lisa M, Ringel Yehuda, Thiny Michelle T, Russo Mark W, Sandler Robert S. The Burden of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases, 2006. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006;101(9):2128–2138. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00723.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lindkvist B, Appelros S, Manjer J, Borgstrom A. Trends in incidence of acute pancreatitis in a Swedish population: is there really an increase? Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology: the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2004;2:831–837. doi: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00355-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

