ELFN2 is a postsynaptic cell adhesion molecule with essential roles in controlling group III mGluRs in the brain and neuropsychiatric behavior
- PMID: 31485013
- PMCID: PMC6874751
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-019-0512-3
ELFN2 is a postsynaptic cell adhesion molecule with essential roles in controlling group III mGluRs in the brain and neuropsychiatric behavior
Abstract
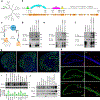
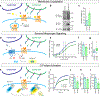
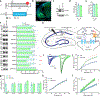
The functional characterization of the GPCR interactome has predominantly focused on intracellular binding partners; however, the recent emergence of transsynaptic GPCR complexes represents an additional dimension to GPCR function that has previously been unaccounted for in drug discovery. Here, we characterize ELFN2 as a novel postsynaptic adhesion molecule with a distinct expression pattern throughout the brain and a selective binding with group III metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in trans. Using a transcellular GPCR signaling platform, we report that ELFN2 critically alters group III mGluR secondary messenger signaling by directly altering G protein coupling kinetics and efficacy. Loss of ELFN2 in mice results in the selective downregulation of group III mGluRs and dysregulated glutamatergic synaptic transmission. Elfn2 knockout (Elfn2 KO) mice also feature a range of neuropsychiatric manifestations including seizure susceptibility, hyperactivity, and anxiety/compulsivity, which can be rescued by pharmacological augmentation of group III mGluRs. Thus, we conclude that extracellular transsynaptic scaffolding by ELFN2 in the brain is a cardinal organizational feature of group III mGluRs essential for their signaling properties and brain function.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS:
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

