A unified mechanism for intron and exon definition and back-splicing
- PMID: 31485080
- PMCID: PMC6939996
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1523-6
A unified mechanism for intron and exon definition and back-splicing
Abstract
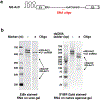
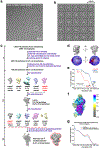
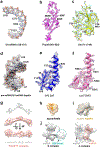
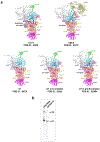
The molecular mechanisms of exon definition and back-splicing are fundamental unanswered questions in pre-mRNA splicing. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the yeast spliceosomal E complex assembled on introns, providing a view of the earliest event in the splicing cycle that commits pre-mRNAs to splicing. The E complex architecture suggests that the same spliceosome can assemble across an exon, and that it either remodels to span an intron for canonical linear splicing (typically on short exons) or catalyses back-splicing to generate circular RNA (on long exons). The model is supported by our experiments, which show that an E complex assembled on the middle exon of yeast EFM5 or HMRA1 can be chased into circular RNA when the exon is sufficiently long. This simple model unifies intron definition, exon definition, and back-splicing through the same spliceosome in all eukaryotes and should inspire experiments in many other systems to understand the mechanism and regulation of these processes.
Figures


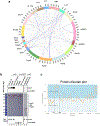
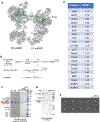



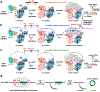
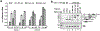
Comment in
-
Intron definition, exon definition and back-splicing revisited.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Nov;20(11):661. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0178-3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31548713 No abstract available.
References
-
- Berget SM Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J Biol Chem 270, 2411–2414 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM122579/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018111/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129325/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM121487/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM121487/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM126157/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM126157/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- GM130673/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- AI094386/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA219847/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103311/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U24GM116792/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI094386/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM130673/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA219847/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1S100D018111/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122579/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 GM116792/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

