Longitudinal characterization of local perfusion of the rat placenta using contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging
- PMID: 31485312
- PMCID: PMC6710660
- DOI: 10.1098/rsfs.2019.0024
Longitudinal characterization of local perfusion of the rat placenta using contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging
Abstract
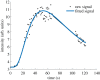
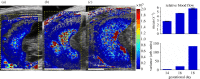
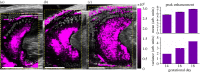
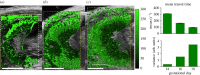
The placenta performs many physiological functions critical for development. Insufficient placental perfusion, due to improper vascular remodelling, has been linked to many pregnancy-related diseases. To study longitudinal in vivo placental perfusion, we have implemented a pixel-wise time-intensity curve (TIC) analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) images. CEUS images were acquired of pregnant Sprague Dawley rats after bolus injections of gas-filled microbubble contrast agents. Conventionally, perfusion can be quantified using a TIC of contrast enhancement in an averaged region of interest. However, the placenta has a complex structure and flow profile, which is insufficiently described using the conventional technique. In this work, we apply curve fitting in each pixel of the CEUS image series in order to quantify haemodynamic parameters in the placenta and surrounding tissue. The methods quantified an increase in mean placental blood volume and relative blood flow from gestational day (GD) 14 to GD18, while the mean transit time of the microbubbles decreased, demonstrating an overall rise in placental perfusion during gestation. The variance of all three parameters increased during gestation, showing that regional differences in perfusion are observable using the pixel-wise TIC approach. Additionally, the high-resolution parametric images show distinct regions of high blood flow developing during late gestation. The developed methods could be applied to assess placental vascular remodelling during the treatment of the pathologies of pregnancy.
Keywords: contrast-enhanced ultrasound; functional imaging; perfusion; placenta; vascular flow.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantifying Molecular Changes in the Preeclamptic Rat Placenta with Targeted Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging.Mol Imaging Biol. 2025 Apr;27(2):274-284. doi: 10.1007/s11307-025-01988-4. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Mol Imaging Biol. 2025. PMID: 40014198 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time placental perfusion on contrast-enhanced ultrasound and parametric imaging analysis in rats at different gestation time and different portions of placenta.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e58986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058986. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23560042 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into uteroplacental perfusion: quantitative analysis using Doppler and contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging.Placenta. 2013 May;34(5):424-31. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2013.01.019. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Placenta. 2013. PMID: 23518453
-
Quantitative evaluation of microvascular blood flow by contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS).Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2011;49(1-4):137-49. doi: 10.3233/CH-2011-1464. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2011. PMID: 22214685 Review.
-
Novel applications of contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging in vascular medicine.Vasa. 2013 Jan;42(1):17-31. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000244. Vasa. 2013. PMID: 23385223 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantifying Molecular Changes in the Preeclamptic Rat Placenta with Targeted Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging.Mol Imaging Biol. 2025 Apr;27(2):274-284. doi: 10.1007/s11307-025-01988-4. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Mol Imaging Biol. 2025. PMID: 40014198 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

