Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sarcoidosis
- PMID: 31485575
- PMCID: PMC6713839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2019.04.006
Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sarcoidosis
Abstract
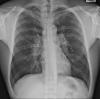
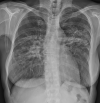
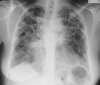
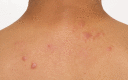
The focus of this review is current knowledge about the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of both pulmonary sarcoidosis and extrapulmonary sarcoidosis. Although intrathoracic involvement is the hallmark of the disease, present in over 90% of patients, sarcoidosis can affect virtually any organ. Clinical presentations of sarcoidosis are diverse, ranging from asymptomatic, incidental findings to organ failure. Diagnosis requires the presence of noncaseating granuloma and compatible presentations after exclusion of other identifiable causes. Spontaneous remission is frequent, so treatment is not always indicated unless the disease is symptomatic or causes progressive organ damage/dysfunction. Glucocorticoids are the cornerstone of treatment of sarcoidosis even though evidence from randomized controlled studies is lacking. Glucocorticoid-sparing agents and biologic agents are often used as second- and third-line therapy for patients who do not respond to glucocorticoids or experience serious adverse effects.
Keywords: ATS, American Thoracic Society; AV, atrioventricular; CMRI, cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; ECG, electrocardiographic; ERS, European Respiratory Society; FDG-PET, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography; FVC, forced vital capacity; GI, gastrointestinal tract; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; PFT, pulmonary function test; TBB, transbronchial lung biopsy; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; WASOG, World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Thomas K.W., Hunninghake G.W. Sarcoidosis. JAMA. 2003;289(24):3300–3303. - PubMed
-
- Chen E.S., Moller D.R. Sarcoidosis—scientific progress and clinical challenges. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(8):457–467. - PubMed
-
- Chen E.S., Moller D.R. Etiology of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2008;29(3):365–377. - PubMed
-
- Rybicki B.A., Major M., Popovich J., Jr., Maliarik M.J., Iannuzzi M.C. Racial differences in sarcoidosis incidence: a 5-year study in a health maintenance organization. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145(3):234–241. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

