Design and Comprehension Testing of Tailored Asthma Control Infographics for Adults with Persistent Asthma
- PMID: 31486056
- PMCID: PMC6727064
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1693713
Design and Comprehension Testing of Tailored Asthma Control Infographics for Adults with Persistent Asthma
Abstract
Background: Adherence to daily inhaled corticosteroid medication is important for asthma control but low health literacy is a barrier to comprehension of control status and may contribute to medication nonadherence. Infographics tailored with patients' own data can support comprehension of health status, but these have not been applied to asthma successfully.
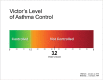
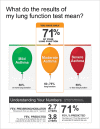
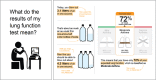
Objectives: This two-phased study developed and tested tailored infographics of (1) scores on the Asthma Control Questionnaire (ACQ), a self-report measure of symptom burden, and (2) pulmonary function test (PFT) results. The infographics are intended for use as communication and adherence-promotion tools in clinical interactions.
Methods: For both phases, participants (18+ years, English- or Spanish-speaking, persistent asthma) were recruited through two primary care clinics. In Phase I, we used a hybrid iterative participatory design process to refine prototype designs. In Phase II, we conducted individual comprehension assessment interviews with the finalized designs. Infographics were hand-tailored for each participant using their ACQ score and PFT results collected at the start of the interview. Two independent raters scored interview transcripts for gist and verbatim comprehension based on a predetermined rubric.
Results: The five Phase I design sessions led to final prototypes that participants (n = 21) considered appealing and easy to comprehend. All Phase II participants (n = 10) demonstrated complete gist and verbatim comprehension. Participants reacted favorably to receiving their information via infographics and expressed intentions to engage in self-management behaviors (e.g., medication adherence, smoking cessation, weight loss, and review of their care plan) in response to the information.
Conclusion: This study provides preliminary evidence that infographics can support comprehension of asthma control status and promote self-management intentions among adults with persistent asthma. Infographics can be programmed into electronic health records and/or standalone applications to allow for instant tailoring at the point of care.
Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York.
Conflict of interest statement
M.G. serves as an advisor to Astra Zeneca and on the Advisory Board to Teva. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in the research. M.G. reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Teva, outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program.Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007 J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007120(5, Suppl):S94–S138. - PubMed
-
- Murphy KR, Meltzer EO, Blaiss MS, Nathan RA, Stoloff SW, Doherty DE. Asthma management and control in the United States: results of the 2009 Asthma Insight and Management survey. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012;33(01):54–64. - PubMed
-
- Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Bailey C et al.Trends in asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality in the United States, 2001-2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2012;(94):1–8. - PubMed

