Dyslipidemia in retinal metabolic disorders
- PMID: 31486227
- PMCID: PMC6783651
- DOI: 10.15252/emmm.201910473
Dyslipidemia in retinal metabolic disorders
Abstract
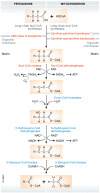
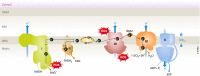
The light-sensitive photoreceptors in the retina are extremely metabolically demanding and have the highest density of mitochondria of any cell in the body. Both physiological and pathological retinal vascular growth and regression are controlled by photoreceptor energy demands. It is critical to understand the energy demands of photoreceptors and fuel sources supplying them to understand neurovascular diseases. Retinas are very rich in lipids, which are continuously recycled as lipid-rich photoreceptor outer segments are shed and reformed and dietary intake of lipids modulates retinal lipid composition. Lipids (as well as glucose) are fuel substrates for photoreceptor mitochondria. Dyslipidemia contributes to the development and progression of retinal dysfunction in many eye diseases. Here, we review photoreceptor energy demands with a focus on lipid metabolism in retinal neurovascular disorders.
Keywords: FGF21; dyslipidemia; photoreceptor; retinal metabolism; β-oxidation.
© 2019 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ait‐Ali N, Fridlich R, Millet‐Puel G, Clerin E, Delalande F, Jaillard C, Blond F, Perrocheau L, Reichman S, Byrne LC et al (2015) Rod‐derived cone viability factor promotes cone survival by stimulating aerobic glycolysis. Cell 161: 817–832 - PubMed
-
- Akula JD, Hansen RM, Tzekov R, Favazza TL, Vyhovsky TC, Benador IY, Mocko JA, McGee D, Kubota R, Fulton AB (2010) Visual cycle modulation in neurovascular retinopathy. Exp Eye Res 91: 153–161 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EY029238/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX003604/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- 1U54HD090255/Boston Children's Hospital (BCH)/International
- DNR# #2016-01131/The Swedish Research Council/International
- CA 1940/1-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)/International
- 1R24EY024868/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)/International
- U54 HD090255/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 89282/Blind Children's Center/International
- R24 EY024864/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Manpei Suzuki Diabetes Foundation/International
- ALFGBG-717971/De Blindas Vanner and Kronprinsessan Margaretas Arbetsnamnd for synskadade/International
- 305485/European Commission (EC)/International
- R01 EY017017/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022938/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 96307/BCH | Manton Center for Orphan Disease Research, Boston Children's Hospital (Manton Center)/International
- R01EY030140/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- EY017017/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)/International
- #7192039/Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation/International
- R01 EY030140/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States

