Elevated Serum Levels of Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1/Chemokine C-C Motif Ligand 2 are Linked to Disease Severity in Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome
- PMID: 31486327
- PMCID: PMC6835162
- DOI: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2019.2019.6.47
Elevated Serum Levels of Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1/Chemokine C-C Motif Ligand 2 are Linked to Disease Severity in Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Elevated levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 have been identified in fibromyalgia patients.
Aims: To examine the potential association among serum levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 with disease severity of fibromyalgia.
Study design: Cross-sectional study.
Methods: Seventy-nine female patients with fibromyalgia and 75 healthy normal controls were included in our study. Serum levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 were detected by enzyme-linked immune sorbent assays. The existence of tender points was evaluated based on the standardized manual tender point examination. Pressure pain thresholds at the knees, and bilateral trapezius muscles were measured with an algometer. A visual analog scale and the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire were utilized to assess the degree of pain and functional abilities.
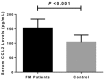
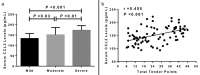
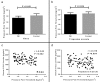
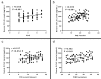
Results: Serum levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 were significantly greater in patients with fibromyalgia compared with healthy controls (151.6±31.9 pg/mL vs 103.3±25.2 pg/mL, p<0.001). Patients with severe fibromyalgia had significantly higher serum levels of chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 than patients with mild and moderate fibromyalgia (173.1±21.9 pg/mL vs 151.0.0±35.1 pg/mL, p=0.01). Patients with moderate fibromyalgia revealed markedly augmented serum levels of chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 compared with patients with mild fibromyalgia (151.0±35.1 pg/mL vs 133.3±23.9 pg/mL, p=0.03). Serum levels of chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 were positively associated with tender point scores (r=0.455, p<0.001). In addition, serum levels of chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 were positively associated with pressure pain thresholds in both knees and bilateral trapezius muscles (knees: r=-0.349, p=0.002; trapezius muscles: r=-0.318, p=0.004). Finally, we found elevated serum levels of chemokine C-C motif ligand were also positively associated with the visual analog scale (r=0.368, p=0.001), and the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire score (r=0.401, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Elevated serum levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 are linked to disease severity of fibromyalgia. Therapeutic interventions inhibiting monocyte chemotactic protein-1/chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 in fibromyalgia deserve additional studies.
Keywords: fibromyalgia; Chemokine CCL2; monocyte chemotactic protein-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated CCL2/MCP-1 Levels are Related to Disease Severity in Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Patients.Clin Lab. 2016 Nov 1;62(11):2173-2181. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2016.160408. Clin Lab. 2016. PMID: 28164676
-
Associations Between Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1 in Plasma and First-Time Coronary Events: A Nested Case-Control Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Sep 13;5(9):e002851. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002851. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27625345 Free PMC article.
-
Serum and synovial fluid chemokine ligand 2/monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 concentrations correlates with symptomatic severity in patients with knee osteoarthritis.Ann Clin Biochem. 2015 Mar;52(Pt 2):276-82. doi: 10.1177/0004563214545117. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Ann Clin Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25005456
-
Correlation of Serum CCL3/MIP-1α Levels with Disease Severity in Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Females.Balkan Med J. 2018 Jul 24;35(4):320-325. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.1165. Epub 2018 Apr 15. Balkan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29666038 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between osteoarthritis and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Nov 10;15(1):516. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-02045-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33168099 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perfectionism and Pain Intensity in Women with Fibromyalgia: Its Influence on Activity Avoidance from The Contextual Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 14;17(22):8442. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228442. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33202698 Free PMC article.
-
Pain and the biochemistry of fibromyalgia: patterns of peripheral cytokines and chemokines contribute to the differentiation between fibromyalgia and controls and are associated with pain, fat infiltration and content.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 18;5:1288024. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2024.1288024. eCollection 2024. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38304854 Free PMC article.
-
A Correlation Between the Pathogenic Processes of Fibromyalgia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome in the Middle-Aged Population: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Oct 4;14(10):e29923. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29923. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36381861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liedberg GM, Henriksson CM. Factors of importance for work disability in women with fibromyalgia: an interview study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;47:266–74. - PubMed
-
- Talotta R, Bazzichi L, Di Franco M, Casale R, Batticciotto A, Gerardi MC, et al. One year in review 2017: fibromyalgia. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Sumpton JE, Moulin DE. Fibromyalgia. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;119:513–27. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Walitt BT, Katz RS, Häuser W. Social security work disability and its predictors in patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2014;66:1354–63. - PubMed
-
- Clauw DJ, D'Arcy Y, Gebke K, Semel D, Pauer L, Jones KD. Normalizing fibromyalgia as a chronic illness. Postgrad Med. 2018;130:9–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
