An analysis of the IS 6/IS 26 family of insertion sequences: is it a single family?
- PMID: 31486766
- PMCID: PMC6807381
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000291
An analysis of the IS 6/IS 26 family of insertion sequences: is it a single family?
Abstract
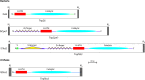
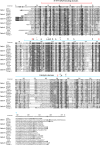
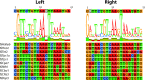
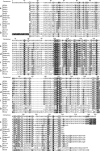
The relationships within a curated set of 112 insertion sequences (ISs) currently assigned to the IS6 family, here re-named the IS6/IS26 family, in the ISFinder database were examined. The encoded DDE transposases include a helix-helix-turn-helix (H-HTH) potential DNA binding domain N-terminal to the catalytic (DDE) domain, but 10 from Clostridia include one or two additional N-terminal domains. The transposase phylogeny clearly separated 75 derived from bacteria from 37 from archaea. The longer bacterial transposases also clustered separately. The 65 shorter bacterial transposases, including Tnp26 from IS26, formed six clades but share significant conservation in the H-HTH domain and in a short extension at the N-terminus, and several amino acids in the catalytic domain are completely or highly conserved. At the outer ends of these ISs, 14 bp were strongly conserved as terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) with the first two bases (GG) and the seventh base (G) present in all except one IS. The longer bacterial transposases are only distantly related to the short bacterial transposases, with only some amino acids conserved. The TIR consensus was longer and only one IS started with GG. The 37 archaeal transposases are only distantly related to either the short or the long bacterial transposases and different residues were conserved. Their TIRs are loosely related to the bacterial TIR consensus but are longer and many do not begin with GG. As they do not fit well with most bacterial ISs, the inclusion of the archaeal ISs and the longer bacterial ISs in the IS6/IS26 family is not appropriate.
Keywords: IS26; ISFinder; insertion sequence; phylogenetic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Campbell A, Berg DE, Lederberg EM, Starlinger P, Botstein D, et al. Nomenclature of transposable elements in prokaryotes. In: Shapiro JA, editor. DNA Insertion Elements, Plasmids and Episomes. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1977. pp. 15–22.
-
- Galas DJ, Chandler M. Bacterial insertion sequences. In: Berg DE, Howe MM, editors. Mobile DNA. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1989. pp. 109–162.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

