Standardized Emblica officinalis fruit extract inhibited the activities of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and displayed antioxidant potential
- PMID: 31487036
- PMCID: PMC6973029
- DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.10020
Standardized Emblica officinalis fruit extract inhibited the activities of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and displayed antioxidant potential
Abstract
Background: Emblica officinalis, known as amla in Ayurveda, has been used as a folk medicine to treat numerous pathological conditions, including diabetes. However, the novel extract of E. officinalis fruit extract (amla fruit extract, AFE, Saberry®) containing 100 g kg-1 β-glucogallin along with hydrolyzable tannins has not yet been extensively studied for its antidiabetic potential.
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of AFE and its stability during gastric stress as well as its thermostability.
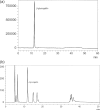
Methods: The effect of AFE on the inhibition of pancreatic α-amylase and salivary α-amylase enzymes was studied using starch and yeast α-glucosidase enzyme using 4-nitrophenyl α-d-glucopyranoside as substrate. Further, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging and reactive oxygen species inhibition assay was performed against AFE.
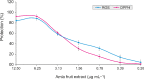
Results: AFE potently inhibited the activities of α-amylase and α-glucosidase in a concentration-dependent manner with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50 ) values of 135.70 μg mL-1 and 106.70 μg mL-1 respectively. Furthermore, it also showed inhibition of α-glucosidase (IC50 562.9 μg mL-1 ) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4; IC50 3770 μg mL-1 ) enzyme activities. AFE is a potent antioxidant showing a free radical scavenging activity (IC50 2.37 μg mL-1 ) and protecting against cellular reactive oxygen species (IC50 1.77 μg mL-1 ), and the effects elicited could be attributed to its phytoconstituents.
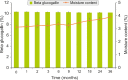
Conclusion: AFE showed significant gastric acid resistance and was also found to be thermostable against wet heat. Excellent α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and DPP-4 inhibitory activities of AFE, as well as antioxidant activities, strongly recommend its use for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. © 2019 The Authors. Journal of The Science of Food and Agriculture published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society of Chemical Industry.
Keywords: DPP-4; Saberry®; amla fruit extract; type 2 diabetes mellitus; α-amylase; α-glucosidase; β-glucogallin.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of The Science of Food and Agriculture published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society of Chemical Industry.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by the Sami Labs Limited/Sabinsa Corporation. The authors are employees of Sabinsa Corporation/Sami Labs Limited, manufacturer and marketer of Saberry® (AFE). The funder did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Hockaday TDR, Hockaday JM, Mann JI and Turner RC, Prospective comparison of modified fat‐high‐carbohydrate with standard low‐carbohydrate dietary advice in the treatment of diabetes: one year follow‐up study. Br J Nutr 39:357–362 (1978). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

