Pneumonia: host susceptibility and shared genetics with pulmonary function and other traits
- PMID: 31487037
- PMCID: PMC6857187
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13367
Pneumonia: host susceptibility and shared genetics with pulmonary function and other traits
Abstract
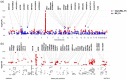
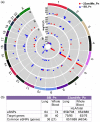
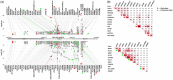
Pneumonia is a common and severe infectious lung disease. Host genetics, together with underlying medical and lifestyle conditions, determine pneumonia susceptibility. We performed a secondary analysis of the results of two genome-wide studies for pneumonia in 23andMe participants (40 600 cases/90 039 controls) (Tian et al., 2017) and UK Biobank (BB) participants (12 614 cases/324 585 controls) (via the Global Biobank Engine) and used the GTEx database to correlate the results with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) data in lung and whole blood. In the 23andMe pneumonia single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) set, 177 genotyped SNPs in the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) region satisfied the genome-wide significance level, P ≤ 5·0E-08. Several target genes (e.g. C4A, VARS2, SFTA2, HLA-C, HLA-DQA2) were unidirectionally regulated by many HLA eSNPs associated with a higher risk of pneumonia. In lung, C4A transcript was up-regulated by 291 pneumonia risk alleles spanning the half the HLA region. Among SNPs correlated with the expression levels of SFTA2 and VARS2, approximately 75% overlapped: all risk alleles were associated with VARS2 up-regulation and SFTA2 down-regulation. To find shared gene loci between pneumonia and pulmonary function (PF), we used data from the Global Biobank Engine and literature on genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of PF in general populations. Numerous gene loci overlapped between pneumonia and PF: 28·8% in the BB data set and 49·2% in the 23andMe data set. Enrichment analysis within the database of Genotypes and Phenotypes (dbGaP) and National Human Genome Research Institute-European Bioinformatics Institute (NHGRI-EBI) Catalog of pneumonia and pneumonia/PF gene sets identified significant overlap between these gene sets and genes related to inflammatory, developmental, neuropsychiatric and cardiovascular and obesity-related traits.
Keywords: C4A; eQTLs; genetic susceptibility; pneumonia; pulmonary function.
© 2019 British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of VARS2-SFTA2 polymorphisms with the risk of chronic hepatitis B in a Korean population.Liver Int. 2015 Aug;35(8):1934-40. doi: 10.1111/liv.12740. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25404243
-
Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) in human placentas suggest developmental origins of complex diseases.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Sep 1;26(17):3432-3441. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx265. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28854703 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial vezatin and its association with endometriosis risk.Hum Reprod. 2016 May;31(5):999-1013. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew047. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27005890
-
Comprehensive identification of pleiotropic loci for body fat distribution using the NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies.Obes Rev. 2019 Mar;20(3):385-406. doi: 10.1111/obr.12806. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Obes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565845 Review.
-
A Data-Driven Review of the Genetic Factors of Pregnancy Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 11;21(9):3384. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093384. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32403311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Wearing Medical Masks on Perioperative Respiratory Complications in Older Adults with Hip Fracture: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Clin Interv Aging. 2021 Nov 19;16:1967-1974. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S333238. eCollection 2021. Clin Interv Aging. 2021. PMID: 34824528 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-C*04:01 Affects HLA Class I Heterozygosity and Predicted Affinity to SARS-CoV-2 Peptides, and in Combination With Age and Sex of Armenian Patients Contributes to COVID-19 Severity.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 3;13:769900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.769900. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35185875 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-wide association study of COVID-19 severity with respiratory failure.EBioMedicine. 2021 Apr;66:103339. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103339. Epub 2021 Apr 15. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 33867313 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics analysis of lung tissue reveals protein makers for the lung injury of adjuvant arthritis rats.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Sep;28(3):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13051. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37449522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farr BM, Woodhead MA, Macfarlane JT et al Risk factors for community‐acquired pneumonia diagnosed by general practitioners in the community. Respir Med 2000; 94:422–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

