Linked dual-class HIV resistance mutations are associated with treatment failure
- PMID: 31487271
- PMCID: PMC6795402
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.130118
Linked dual-class HIV resistance mutations are associated with treatment failure
Abstract
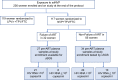
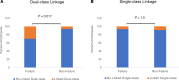
We hypothesized that HIV-1 with dual-class but not single-class drug resistance mutations linked on the same viral genome, present in the virus population before initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART), would be associated with failure of ART to suppress viremia. To test this hypothesis, we utilized an ultrasensitive single-genome sequencing assay that detects rare HIV-1 variants with linked drug resistance mutations (DRMs). A case (ART failure) control (nonfailure) study was designed to assess whether linkage of DRMs in pre-ART plasma samples was associated with treatment outcome in the nevirapine/tenofovir/emtricitabine arm of the AIDS Clinical Trials Group A5208/Optimal Combined Therapy After Nevirapine Exposure (OCTANE) Trial 1 among women who had received prior single-dose nevirapine. Ultrasensitive single-genome sequencing revealed a significant association between pre-ART HIV variants with DRMs to 2 drug classes linked on the same genome (dual class) and failure of combination ART with 3 drugs to suppress viremia. In contrast, linked, single-class DRMs were not associated with ART failure. We conclude that linked dual-class DRMs present before the initiation of ART are associated with ART failure, whereas linked single-class DRMs are not.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00089505.
Keywords: AIDS/HIV; Drug therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- European AIDS Clinical Society. EACS Guidelines Version 9.0. EACS website. http://www.eacsociety.org/files/guidelines_9.0 Accessed September 17, 2019.
-
- Dybul M, Fauci AS, Bartlett JG, Kaplan JE, Pau AK; Panel on Clinical Practices for Treatment of HIV. Guidelines for using antiretroviral agents among HIV-infected adults and adolescents. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(5 Pt 2):381–433. - PubMed
-
- Cozzi-Lepri A, et al. Low-frequency drug-resistant HIV-1 and risk of virological failure to first-line NNRTI-based ART: a multicohort European case-control study using centralized ultrasensitive 454 pyrosequencing. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015;70(3):930–940. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku426. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069453/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI032775/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069453/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069518/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069426/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069436/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069426/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA200421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069455/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI108568/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

