Burkholderia pseudomallei, the causative agent of melioidosis, is rare but ecologically established and widely dispersed in the environment in Puerto Rico
- PMID: 31487287
- PMCID: PMC6748447
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007727
Burkholderia pseudomallei, the causative agent of melioidosis, is rare but ecologically established and widely dispersed in the environment in Puerto Rico
Abstract
Background: Burkholderia pseudomallei is a soil-dwelling bacterium and the causative agent of melioidosis. The global burden and distribution of melioidosis is poorly understood, including in the Caribbean. B. pseudomallei was previously isolated from humans and soil in eastern Puerto Rico but the abundance and distribution of B. pseudomallei in Puerto Rico as a whole has not been thoroughly investigated.
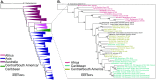
Methodology/principal findings: We collected 600 environmental samples (500 soil and 100 water) from 60 sites around Puerto Rico. We identified B. pseudomallei by isolating it via culturing and/or using PCR to detect its DNA within complex DNA extracts. Only three adjacent soil samples from one site were positive for B. pseudomallei with PCR; we obtained 55 isolates from two of these samples. The 55 B. pseudomallei isolates exhibited fine-scale variation in the core genome and contained four novel genomic islands. Phylogenetic analyses grouped Puerto Rico B. pseudomallei isolates into a monophyletic clade containing other Caribbean isolates, which was nested inside a larger clade containing all isolates from Central/South America. Other Burkholderia species were commonly observed in Puerto Rico; we cultured 129 isolates from multiple soil and water samples collected at numerous sites around Puerto Rico, including representatives of B. anthina, B. cenocepacia, B. cepacia, B. contaminans, B. glumae, B. seminalis, B. stagnalis, B. ubonensis, and several unidentified novel Burkholderia spp.
Conclusions/significance: B. pseudomallei was only detected in three soil samples collected at one site in north central Puerto Rico with only two of those samples yielding isolates. All previous human and environmental B. pseudomallei isolates were obtained from eastern Puerto Rico. These findings suggest B. pseudomallei is ecologically established and widely dispersed in the environment in Puerto Rico but rare. Phylogeographic patterns suggest the source of B. pseudomallei populations in Puerto Rico and elsewhere in the Caribbean may have been Central or South America.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Martina P, Leguizamon M, Prieto CI, Sousa SA, Montanaro P, Draghi WO, et al. Burkholderia puraquae sp. nov., a novel species of the Burkholderia cepacia complex isolated from hospital settings and agricultural soils. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology. 2018;68(1):14–20. Epub 2017/11/03. 10.1099/ijsem.0.002293 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuanyok A, Mayo M, Scholz H, Hall CM, Allender CJ, Kaestli M, et al. Burkholderia humptydooensis sp. nov., a New Species Related to Burkholderia thailandensis and the Fifth Member of the Burkholderia pseudomallei Complex. Applied and environmental microbiology. 2017;83(5). Epub 2016/12/18. 10.1128/AEM.02802-16 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vandamme P, Peeters C, De Smet B, Price EP, Sarovich DS, Henry DA, et al. Comparative Genomics of Burkholderia singularis sp. nov., a Low G+C Content, Free-Living Bacterium That Defies Taxonomic Dissection of the Genus Burkholderia. Frontiers in microbiology. 2017;8:1679 Epub 2017/09/22. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01679 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

