Protein model accuracy estimation based on local structure quality assessment using 3D convolutional neural network
- PMID: 31487288
- PMCID: PMC6728020
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221347
Protein model accuracy estimation based on local structure quality assessment using 3D convolutional neural network
Abstract
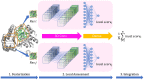
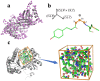
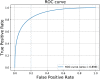
In protein tertiary structure prediction, model quality assessment programs (MQAPs) are often used to select the final structural models from a pool of candidate models generated by multiple templates and prediction methods. The 3-dimensional convolutional neural network (3DCNN) is an expansion of the 2DCNN and has been applied in several fields, including object recognition. The 3DCNN is also used for MQA tasks, but the performance is low due to several technical limitations related to protein tertiary structures, such as orientation alignment. We proposed a novel single-model MQA method based on local structure quality evaluation using a deep neural network containing 3DCNN layers. The proposed method first assesses the quality of local structures for each residue and then evaluates the quality of whole structures by integrating estimated local qualities. We analyzed the model using the CASP11, CASP12, and 3D-Robot datasets and compared the performance of the model with that of the previous 3DCNN method based on whole protein structures. The proposed method showed a significant improvement compared to the previous 3DCNN method for multiple evaluation measures. We also compared the proposed method to other state-of-the-art methods. Our method showed better performance than the previous 3DCNN-based method and comparable accuracy as the current best single-model methods; particularly, in CASP11 stage2, our method showed a Pearson coefficient of 0.486, which was better than those of the best single-model methods (0.366-0.405). A standalone version of the proposed method and data files are available at https://github.com/ishidalab-titech/3DCNN_MQA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep convolutional networks for quality assessment of protein folds.Bioinformatics. 2018 Dec 1;34(23):4046-4053. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty494. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29931128
-
P3CMQA: Single-Model Quality Assessment Using 3DCNN with Profile-Based Features.Bioengineering (Basel). 2021 Mar 19;8(3):40. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8030040. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33808604 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of 8-state protein secondary structures by a novel deep learning architecture.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Aug 3;19(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2280-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30075707 Free PMC article.
-
MASS: predict the global qualities of individual protein models using random forests and novel statistical potentials.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Jul 6;21(Suppl 4):246. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3383-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32631256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances and challenges in protein complex model accuracy estimation.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Apr 21;23:1824-1832. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.04.049. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38707538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3-Dimensional convolutional neural networks for predicting StarCraft Ⅱ results and extracting key game situations.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 3;17(3):e0264550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264550. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35239703 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning to estimate the local quality of protein crystal structures.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 8;11(1):23599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02948-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34880321 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning for Protein-Protein Interaction Site Prediction.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2361:263-288. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1641-3_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34236667
-
Decoy selection for protein structure prediction via extreme gradient boosting and ranking.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Dec 9;21(Suppl 1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3523-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33297949 Free PMC article.
-
Fast predictions of liquid-phase acid-catalyzed reaction rates using molecular dynamics simulations and convolutional neural networks.Chem Sci. 2020 Oct 19;11(46):12464-12476. doi: 10.1039/d0sc03261a. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34094451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonneau R, Tsai J, Ruczinski J, Chivian D, Rohl C, Strauss CE, et al. Rosetta in CASP4: Progress in ab initio protein structure prediction. Proteins. 2001;45(Suppl 5): 119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

