Regulation of the amount of ceramide-1-phosphate synthesized in differentiated human podocytes
- PMID: 31487557
- PMCID: PMC6832884
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158517
Regulation of the amount of ceramide-1-phosphate synthesized in differentiated human podocytes
Abstract
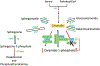
Sphingolipids have important functions as structural components of cells but they also function as signaling molecules regulating different cellular processes such as apoptosis, cell proliferation, cell migration, cell division and inflammation. Hence, a tight regulation of the sphingolipid homeostasis is essential to maintain proper cellular functions. Mammalian ORMDL proteins are orthologues of the yeast ORM1/2 proteins, which regulate ceramide synthesis in yeast. ORMDL proteins inhibit serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), the enzyme regulating a rate-limiting step of the sphingolipid pathway to control the levels of ceramides and other sphingolipids. Sphingomyelinase phosphodiesterase like 3b (SMPDL3b) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored protein in the plasma membrane (PM) and determines membrane fluidity in macrophages. We previously showed that differential expression of SMPDL3b alters the availability of Ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P) in human podocytes, which are terminally differentiated cells of the kidney filtration barrier. This observation lead us to investigate if SMPDL3b controls C1P availability in human podocytes by interfering with ceramide kinase (CERK) expression and function. We found that SMPDL3b interacts with CERK and can bind to C1P in vitro. Furthermore, CERK expression is reduced when SMPDL3b expression is silenced. These observations led us to propose that one of the mechanisms by which SMPDL3b influences the amount of C1P available in the podocytes is by interfering with the function of CERK thereby maintaining a balance in the levels of the C1P in podocytes.
Keywords: Ceramide-1-phosphate; Podocytes; SMPDL3b; Sphingolipids.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
G.W.B., A.F., and S.M. are inventors on pending or issued patents (US10,183,038, US10,052,345) aimed to diagnose or treat proteinuric renal diseases. They stand to gain royalties from their future commercialization. A.F. is Chief Scientific Officer of L&F Health LLC and is consultant for Variant Pharmaceutical. A.F. is Chief Medical Officer of LipoNexT, LLC. SKM, AM have no any competing interests.
Figures
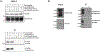
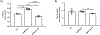
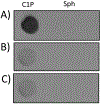
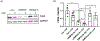
Similar articles
-
SMPDL3b modulates radiation-induced DNA damage response in renal podocytes.FASEB J. 2022 Oct;36(10):e22545. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100186RR. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 36094323 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b mediates radiation-induced damage of renal podocytes.FASEB J. 2017 Feb;31(2):771-780. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600618R. Epub 2016 Nov 11. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 27836988 Free PMC article.
-
SMPDL3b modulates insulin receptor signaling in diabetic kidney disease.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 19;10(1):2692. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10584-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31217420 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide kinase: the first decade.Cell Signal. 2011 Jun;23(6):999-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.11.012. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21111813 Review.
-
Ceramide-1-phosphate in phagocytosis and calcium homeostasis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:131-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6741-1_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20919651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS.J Cell Signal. 2020 Sep;1(3):56-69. doi: 10.33696/Signaling.1.013. J Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32914148 Free PMC article.
-
Podocyte Sphingolipid Signaling in Nephrotic Syndrome.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Apr 17;55(S4):13-34. doi: 10.33594/000000356. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33861526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implication of Ceramide Kinase/C1P in Cancer Development and Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 4;14(1):227. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010227. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35008391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipid signaling in kidney diseases.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Mar 1;328(3):F431-F443. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00193.2024. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39933715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Oct;19(10):629-645. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00741-w. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37500941 Review.
References
-
- Holthuis JC, et al., The organizing potential of sphingolipids in intracellular membrane transport. Physiol Rev, 2001. 81(4): p. 1689–723. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Munoz A, The Role of Ceramide 1-Phosphate in Tumor Cell Survival and Dissemination. Adv Cancer Res, 2018. 140: p. 217–234. - PubMed
-
- Granado MH, et al., Ceramide 1-phosphate inhibits serine palmitoyltransferase and blocks apoptosis in alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2009. 1791(4): p. 263–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

